For those of you who have watched the American series “Never Have I Ever” you would have seen Lily D Moore playing the role of Paxton’s sister who has Down syndrome. Although we know in western countries individuals with Down Syndrome are into modeling, tv shows, and even in politics. Did you know that a Kollywood movie named “Kaathuvaakula Rendu Kaadhal” featured Master Bhargav who played Nayantara’s brother role and recently Bengaluru’s Riza Reji has been officially selected for the “Global Down Syndrome Foundation’s annual fashion show” – Be Beautiful, Be Yourself – which features over 20 models with Down syndrome.
All the above examples are another step along the ongoing road of embracing and celebrating the inclusivity of people with Down Syndrome.
History of Down Syndrome
Let’s start with the history of Down syndrome: Down syndrome is named after a British Physician, John Langdon Down in the year 1866. Langdon initially described Down syndrome as Mongolism. The term Down syndrome was not accepted until early 1970.
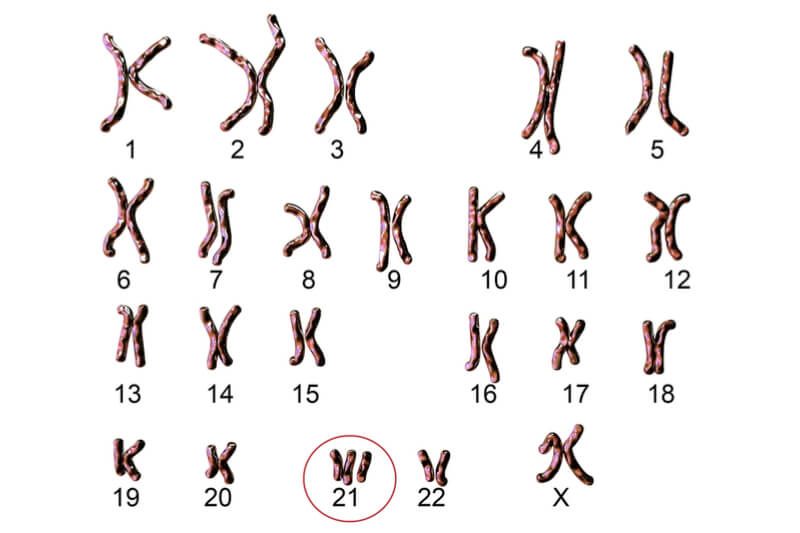
In 1959, a French Pediatrician/ Geneticist Professor Jerome Lejeune discovered that individuals with the syndrome have an extra 21st chromosome. In 1961, National Association for Down syndrome was founded by a group of parents who had children with Down Syndrome to create a support system and raise awareness about the condition.
World Down Syndrome Day is globally celebrated on the 21st of March. This is because the 21st day of the 3rd month symbolizes three copies of the 21 chromosome that is Down syndrome. This year’s theme is “With Us Not For Us”.
What is Down Syndrome?
Before we understand what Down syndrome is, let's understand what chromosomes are: Human beings have 46 chromosomes. We inherit 23 from our mother and 23 from our father. Individuals with Down syndrome have an extra copy of the 21st chromosome which makes them special.
What is the prevalence of Down Syndrome in India?
According to recent research published in 2022, approximately 23,000-29,000 children are born in India every year with Down syndrome.
There are three different kinds of Down syndrome:
- Trisomy 21: An individual has three copies of the 21st chromosome
- Mosaic Trisomy 21: This happens when there is a mix of two kinds of cells, meaning, a few cells have 46 chromosomes, a few cells have 47 chromosomes
- Translocation Trisomy 21: In this type of Down syndrome, the chromosomes remain at 46, but a part 21st chromosome or the entire 21st chromosome may get attached to another chromosome leading to Down syndrome.
Individuals with Down syndrome have distinct features that make them different from all of us. Features include a Small head, small neck, flat nasal bridge, protruding tongue, upward slanting eyes, excessive flexibility etc.
Usually, individuals with Down syndrome can live up to more than 60 years of age but they have a few complications such as global developmental delay, Intellectual disability, cardiac-related conditions, sleep apnea, diabetes, hypothyroidism, obesity, dementia, a few individuals are diagnosed with leukemia as well.
What are the risk factors of Down Syndrome?
- Advanced maternal age: Women above the age of 35 years tend to have an increased risk of having a child with Down syndrome.
- If either of the parents or one of them is a carrier for balanced translocation between chromosome 21 and other chromosomes
- Having a previous child with the syndrome or any first-degree relative with the syndrome increases the risk of a child being born with the same.
Routine tests offered during pregnancy to detect Down syndrome:
Screening Tests
Combined first-trimester screening test: Combined first-trimester screening test measures the biochemical estimation of two parameters: pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and Beta HCG, along with an ultrasound examination of Nuchal Translucency (NT). Elevated levels of NT give an indication of Down syndrome.
Quadruple marker testing: A quadruple marker test is generally done between 15-18 weeks of gestation. The fetal medicine specialist usually checks four biomarkers. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), Estriol (uE3), and Inhibin A. Decreased levels of AFP and uE3 AN Increased levels of HCG and Inhibin A gives an indication of Down syndrome.
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing, also known as Non-Invasive Prenatal Screening (NIPS), screens chromosomal aneuploidies. It is a simple blood test that a pregnant woman can undergo from the 10th week of gestation. The sensitivity and specificity of NIPS for Trisomy 21 are more than 99%
If any of the tests mentioned above are high risk, invasive testing such as Chorionic Villus Sampling or Amniocentesis is offered to a patient.
Services provided at MapMyGenome
MapMyGenome offers genetic counseling services to help you understand the condition and provide you with the right choice of genetic testing.
MapMyGenome also offers clinical genomic testing such as Karyotyping, Qf-PCR, FISH, Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing, Chromosomal Microarray, Whole exome sequencing, etc.
To know more about MapMyGenome clinical genomic testing: https://mapmygenome.in/diagnostic/mother-and-child/
To know more about MapMyGenome Genetic Counseling: https://mapmygenome.in/genetic-counseing/
List of support groups in India
https://downsyndrome.in/
https://downsyndrome.in/support-group/
http://motherandchildschool.com/mac-activities.html
https://guidestarindia.org/Summary.aspx?CCReg=257
https://amritfoundationofindia.in/understand-the-challenges/down-syndrome/