At MapmyGenome™, we believe that informed individuals make healthier choices, so let's delve into the world of thyroid cancer.
Understanding Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer may not be a common topic of conversation, but it's crucial to grasp the fundamentals. The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, plays a vital role in regulating metabolism by producing hormones that regulate heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and weight. A healthy thyroid is a little larger than a quarter. It usually cannot be felt through the skin. However, like any other organ, it can develop cancerous cells.
Categorizing Thyroid Cancer: Understanding Different Types
Just as with any other health condition, thyroid cancer comes in various forms, classified by the types of cells from which it originates. Let's explore the different types of thyroid cancer in a way that makes them easier to understand:
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer: This is the most common type, making up to 80% of thyroid cancer cases. It can happen at any age, but it most often affects people ages 30 to 50. It tends to grow slowly and often spreads to nearby lymph nodes in the neck. The good news is that it responds exceptionally well to treatment, making it highly curable and rarely fatal.
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer: This rare type of thyroid cancer usually affects people older than 50. Accounting for about 15% of thyroid cancer diagnoses, follicular thyroid cancer has a tendency to spread to distant organs like the lungs and bones. This metastatic nature can pose challenges in treatment.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Medullary thyroid cancer is relatively rare, comprising roughly 2% of thyroid cancers. Interestingly, about a quarter of individuals with this type have a family history of the disease, suggesting a genetic connection or faulty gene mutation. Sporadic (not inherited) medullary thyroid cancer affects women more commonly than men and has a peak incidence in the 40-50 years of age range.
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: Among the thyroid cancers, anaplastic thyroid cancer is the most aggressive and challenging to treat. It grows rapidly and often infiltrates nearby tissues and other parts of the body. This rare form accounts for about 2% of thyroid cancer diagnoses and tends to occur in people older than 60.
Recognizing the Signs
Thyroid cancer symptoms can be subtle, so it's essential to be vigilant:
- If you notice a painless lump or swelling in your neck, especially near the thyroid area, get it checked.
- Hoarseness or difficulty speaking can result from the pressure of a thyroid tumor on the vocal cords.
- Persistent difficulty in swallowing could be a sign of an enlarged thyroid.
- Unexplained pain in the throat or neck that doesn't go away should be evaluated.
- If your voice becomes noticeably different, seek medical attention.
- Enlarged or swollen lymph nodes in the neck may indicate thyroid cancer spreading.
- A feeling that close-fitting shirt collars are becoming too tight
Risk Factors and Causes
While the precise cause of most thyroid cancer remains unclear, certain factors can elevate your risk:
- Gender: Thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men.
- Age: Risk increases with age, with most diagnoses occurring between 30 and 60.
- Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation therapy to the head, neck, or chest may increase the risk.
- Family History: A family history of thyroid cancer can elevate your susceptibility.
- Certain inherited genetic syndromes. Some genetic syndromes increase the chances of developing thyroid cancer. These include familial medullary thyroid cancer, multiple endocrine neoplasia, Cowden syndrome, and familial adenomatous polyposis. Thyroid cancer types that can be hereditary are medullary thyroid cancer and papillary thyroid cancer.
Diagnosis and Tests
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. The following tests and procedures are commonly used:
-
Physical Exam and Health History: Your doctor will conduct a thorough examination of your body, including the neck, to check for any signs of disease. They will also gather information about your health history, past illnesses, and treatments.
-
Laryngoscopy: This procedure involves examining the larynx (voice box) using a mirror or a laryngoscope. It helps determine if a thyroid tumor is affecting the movement of your vocal cords.
-
Blood Hormone Studies: A blood sample is taken to measure hormone levels released by various organs and tissues. Abnormal hormone levels, such as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), calcitonin, and antithyroid antibodies, can indicate thyroid disease.
-
Blood Chemistry Studies: Another blood sample is analyzed to measure substances like calcium released by organs and tissues. Abnormal levels of these substances can signal underlying diseases.
-
Thyroid Ultrasound: This painless procedure uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland. It helps assess the size of thyroid nodules and whether they are solid or fluid-filled cysts.
-
CT Scan (CAT Scan): Detailed images of the neck and other areas inside the body are obtained using computed tomography (CT) scanning. This may involve the use of a contrast dye to enhance visibility.
-
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: During this procedure, a thin needle is used to collect small tissue samples from different parts of the thyroid. A pathologist then examines these samples under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
-
Surgical Biopsy: In some cases, a thyroid nodule or one lobe of the thyroid may be removed during surgery. This allows for a closer examination of the cells and tissues to check for signs of cancer.
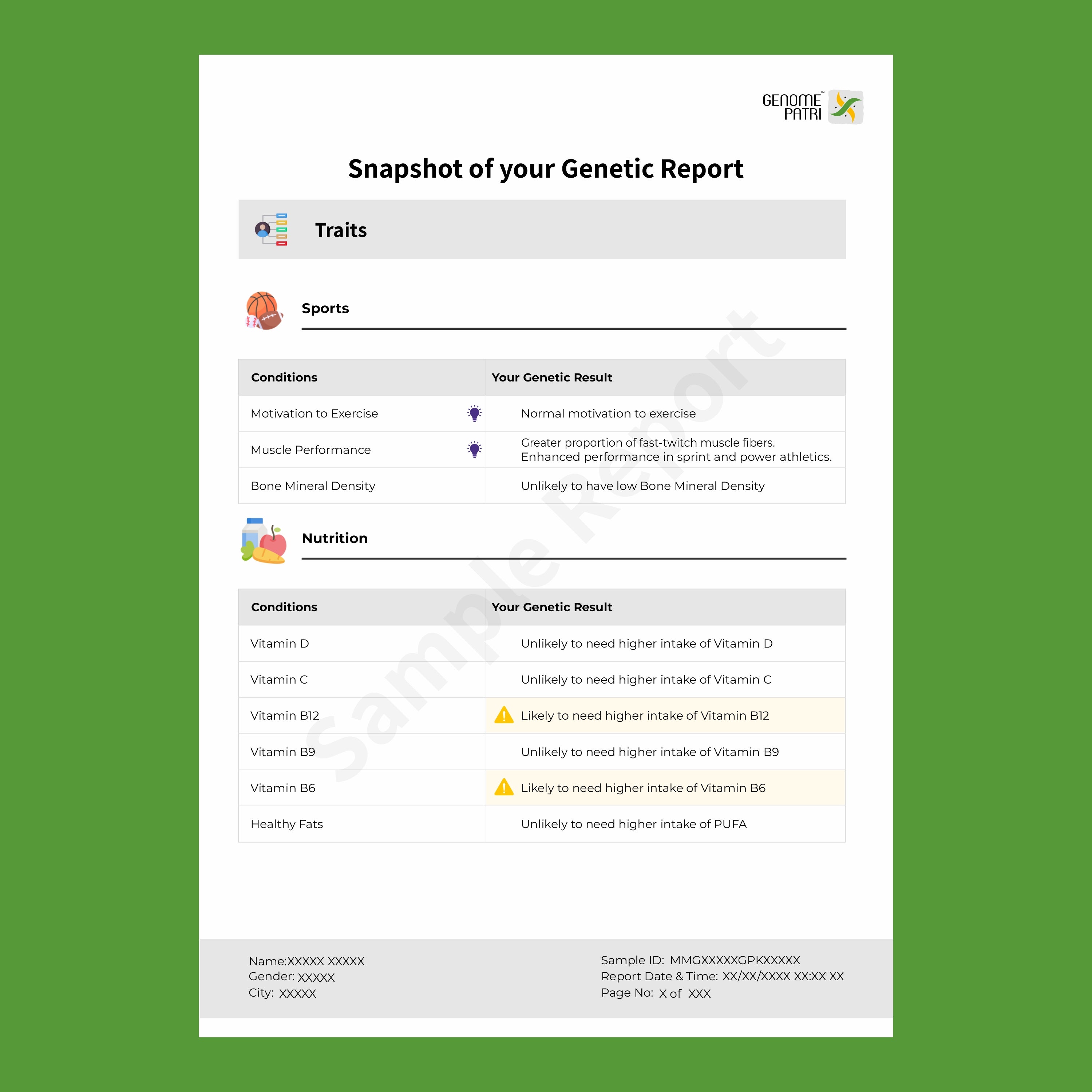
Genetic Testing in Thyroid Cancer
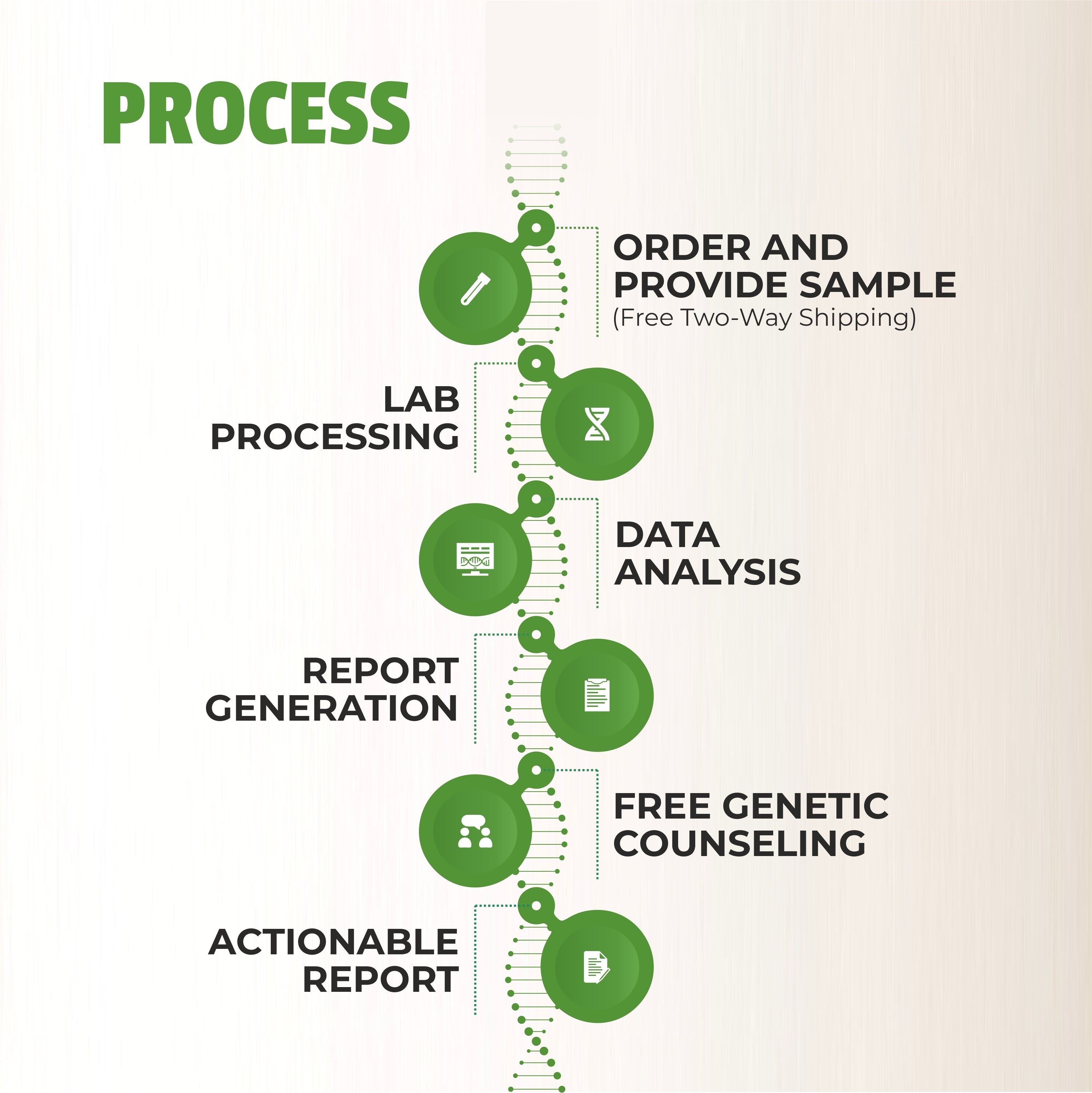
Genetic testing has become a game-changer, especially when you've got a family history of thyroid cancer or other inherited cancer syndromes. Here's why it's a big deal:
- Uncovering Hidden Risks: Genetic testing isn't just about ancestry and fun facts; it's about spotting those sneaky gene variations that can increase your thyroid cancer risk. If your family has a history of multiple cancers or cases of thyroid cancer occurring before the age of 60, it's advisable to consult with a genetic counselor to explore the potential risks associated with gene variations. This is the kind of information you want to uncover.
- Personalized Health Roadmap: Imagine having a GPS for your health. That's what your genetic profile can be. It guides your medical team in crafting a plan that's tailored to you, from screening schedules to treatment strategies.
- It's a Family Affair: This isn't just about you. Your genetic makeup can impact your family too. If you've got a gene variation, your relatives might be at risk. Sharing this knowledge is like giving them a heads-up in the game of health.
- Treatment Clues: Think of genes as your personal cheat codes. Some gene mutations can give your healthcare provider insights into which treatments might work best for you. So, when your healthcare provider knows your genetic playbook, they can choose the most effective game plan.
In the world of genes and genetic testing, think of genetic counselors as your trusted guides. They're experts at helping you and your family understand your genetic information, figure out any risks, and make smart choices. They look at your family history and genes, provide support during testing, explain what the results mean, help you talk about it with your family, and even work with your healthcare team to use your genetic information for better treatments. So, if you're thinking about genetic testing, chatting with a genetic counselor is a clever move to make sense of how your genes can affect your health.
And here at MapmyGenome™, we've got your back! We offer tests like the Genomepatri™ and the Hereditary Cancer Panel and our team of experienced genetic counselors are ready to provide you with excellent insights and guidance. Reach out to MapmyGenome’s genetic counselors to learn more about genetic testing for thyroid cancer. Your health journey just got a whole lot clearer!
Preventing Thyroid Cancer
While you can't guarantee prevention, these steps can help reduce your risk:
Regular Check-ups: Consult your healthcare provider for regular check-ups, especially if you have risk factors.
Limit Radiation Exposure: Avoid unnecessary exposure to radiation, especially in the head, neck, and chest areas.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, and adopt a healthy lifestyle
Prioritize your well-being
Early detection and healthy living can make a significant difference in managing thyroid cancer. As Marcus Valerius Martial put it, 'Life is not merely to be alive but to be well'. At MapmyGenome™, we prioritize your well-being, and we're here to help you navigate your journey to better health.