Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to serious health complications if not managed properly. While lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise play a significant role in the development of diabetes, genetics also has a crucial influence. Understanding your genetic predisposition can empower you to take proactive steps in managing your risk. This blog will delve into how genetic testing can help identify your risk of developing diabetes and why it might be a valuable tool for those with a family history of the condition.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Risk Factors
Diabetes occurs when the body is unable to effectively regulate blood sugar levels. There are two main types of diabetes:
-
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type typically develops in childhood or adolescence and is less influenced by lifestyle factors.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet, but genetics also play a significant role.
In addition to these, gestational diabetes can occur during pregnancy and increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes:
- Family history of diabetes
- Obesity or overweight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet
- High blood pressure
- Age (45 years or older)
- Ethnic background (higher prevalence in certain ethnic groups)
While these factors are well-known, they don’t fully explain why some people develop diabetes and others don’t. This is where genetics come into play.
What is Genetic Testing for Diabetes?
Genetic testing for diabetes involves analyzing your DNA to identify specific genes or gene mutations associated with an increased risk of developing the condition. Researchers have identified several genes that contribute to the risk of type 2 diabetes, including:
-
TCF7L2: Variations in this gene are strongly associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. People with certain variants of this gene are more likely to develop the condition.
-
SLC30A8: This gene plays a role in insulin production. Variations can affect how the pancreas releases insulin in response to blood sugar levels.
-
PPARG: This gene influences how the body stores and uses fat. Mutations in PPARG can lead to insulin resistance, a key factor in type 2 diabetes.
By analyzing these and other genes, genetic testing can provide a clearer picture of your individual risk.
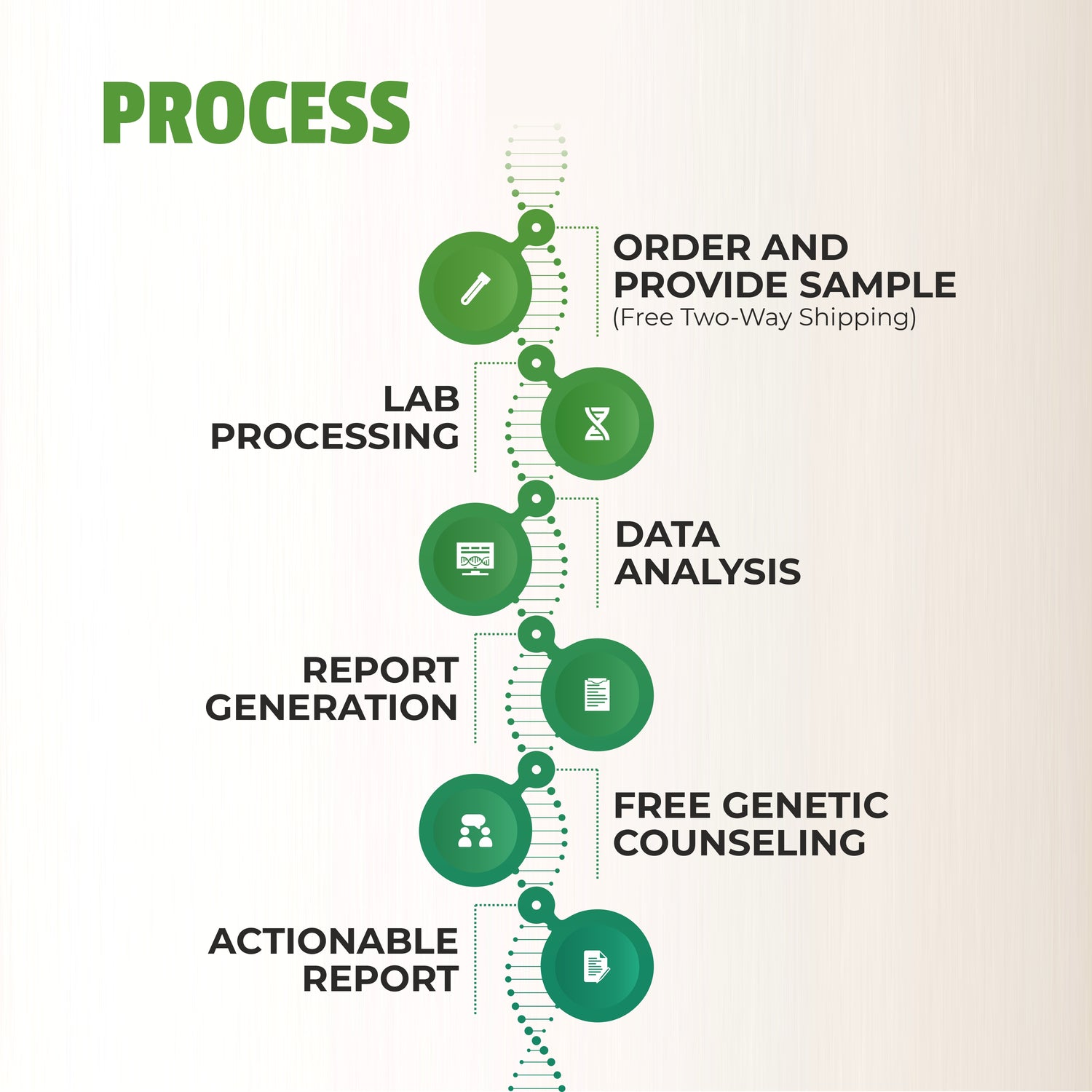
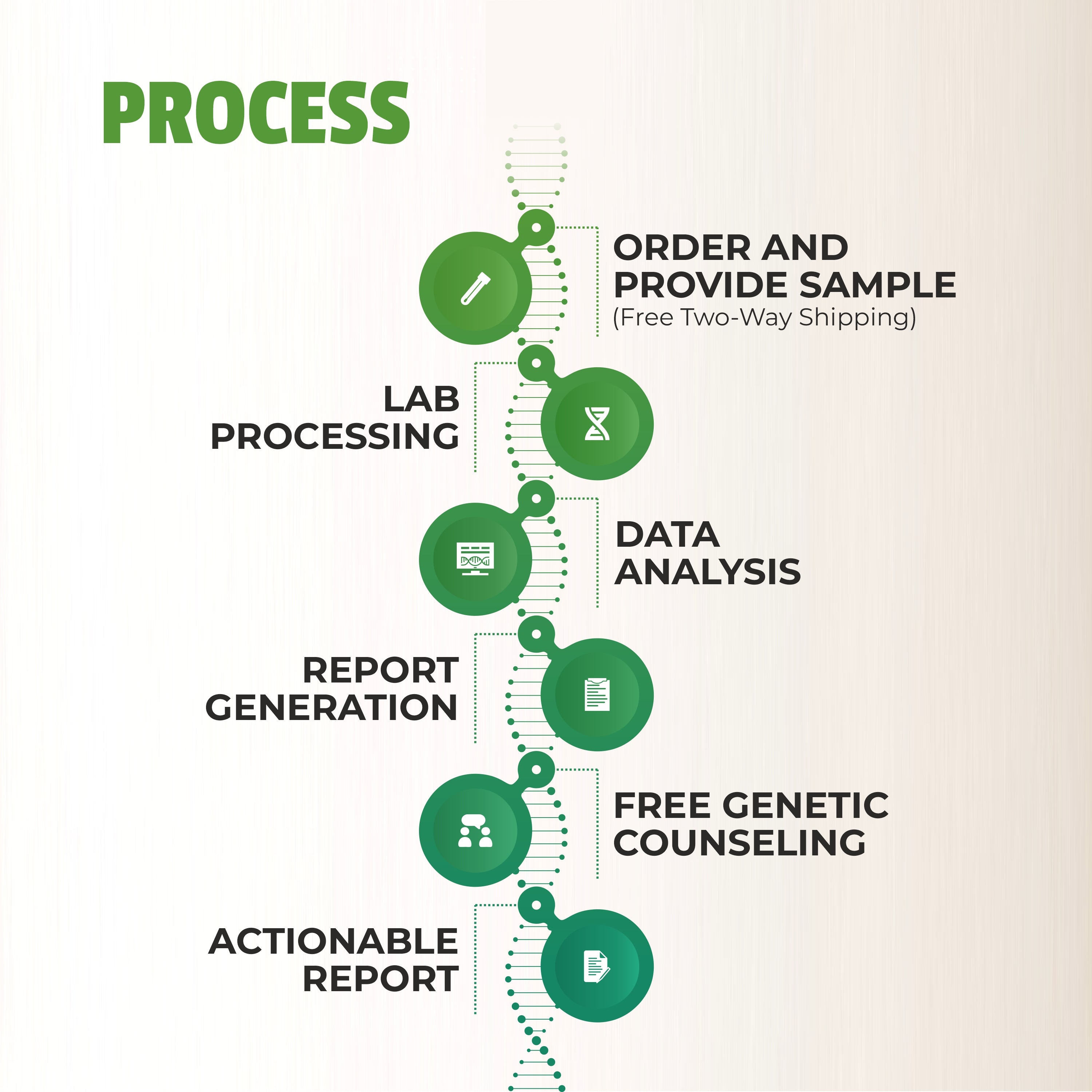
How Genetic Testing Works
The process of genetic testing for diabetes is straightforward and typically involves the following steps:
-
Consultation: You start with a consultation with a healthcare provider or genetic counselor who will assess your medical and family history and discuss the potential benefits of genetic testing.
-
Sample Collection: A DNA sample is collected, usually through a saliva sample or blood draw.
-
Laboratory Analysis: The sample is sent to a lab, where it is analyzed for specific genetic markers associated with diabetes.
-
Results and Interpretation: After a few weeks, the results are sent back to your healthcare provider or genetic counselor, who will explain what they mean for your risk of developing diabetes.
-
Action Plan: Based on your results, you and your healthcare provider can create a personalized plan to manage or reduce your risk. This may include lifestyle changes, more frequent monitoring, or even medication.
The Benefits of Genetic Testing for Diabetes
Genetic testing for diabetes offers several potential benefits:
-
Personalized Risk Assessment: Unlike general risk factors like age or weight, genetic testing provides a personalized assessment based on your unique genetic makeup. This can give you a more accurate understanding of your risk level.
-
Early Intervention: If you are found to have a high genetic risk for diabetes, you can take steps early to manage that risk. This might include adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
-
Targeted Monitoring: Knowing your genetic risk can help you and your healthcare provider decide how often you should be screened for diabetes. More frequent monitoring can lead to early detection and better management if diabetes does develop.
-
Informed Family Planning: If you have a high genetic risk for diabetes, this information can be valuable for family planning. You can take steps to reduce your risk before having children or discuss the potential risk with your healthcare provider.
-
Peace of Mind: For some, genetic testing can provide peace of mind. If your genetic risk is low, you may be less anxious about developing diabetes, though it’s still important to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Limitations and Considerations
While genetic testing for diabetes offers many benefits, it’s important to be aware of its limitations:
-
Not Deterministic: Having a genetic predisposition to diabetes does not mean you will definitely develop the condition. Similarly, a low genetic risk doesn’t mean you are immune. Lifestyle factors remain critical.
-
Ethical and Privacy Concerns: Genetic information is sensitive, and there are concerns about how this data might be used by employers or insurance companies. It’s important to choose a reputable provider that protects your privacy.
-
Cost: Genetic testing can be expensive, and not all insurance plans cover it. However, the cost may be justified if it leads to early intervention and better health outcomes.
-
Complexity of Results: Genetic testing results can be complex and sometimes difficult to interpret. This is why working with a genetic counselor is essential to understand what your results mean and how to act on them.
Taking Action Based on Your Results
If your genetic testing results indicate a higher risk of developing diabetes, there are several proactive steps you can take:
-
Lifestyle Changes: Focus on maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and getting regular physical activity.
-
Regular Monitoring: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your blood sugar levels and other indicators of diabetes.
-
Medication: In some cases, your healthcare provider might recommend medications that can help reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
-
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest research on diabetes and genetic testing. Understanding new developments can help you make informed decisions about your health.
Conclusion: Is Genetic Testing for Diabetes Right for You?
Genetic testing for diabetes is a powerful tool that can help you understand your risk and take proactive steps to protect your health. If you have a family history of diabetes or are concerned about your risk, consider discussing genetic testing with your healthcare provider. While it’s not a guarantee that you will or won’t develop diabetes, the insights gained from genetic testing can guide your healthcare decisions and help you live a healthier, more informed life.
Taking control of your health starts with understanding your risks. With genetic testing, you can move beyond guessing and start planning for a healthier future.