Genetic testing has become an integral part of modern healthcare, offering valuable insights into our genetic makeup and helping to predict, diagnose, and even prevent various health conditions. Whether you're concerned about hereditary diseases, interested in understanding your ancestry, or looking for personalized health recommendations, genetic testing can provide you with critical information tailored to your unique genetic profile.
What is Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing involves analyzing your DNA—the genetic material that carries the instructions for your body's growth, development, and function. By examining specific genes, chromosomes, or proteins, genetic tests can reveal changes or mutations that may lead to health problems. The results of these tests can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Types of Genetic Testing
There are several types of genetic testing, each serving a different purpose:
-
Diagnostic Testing: Used to diagnose a specific genetic condition in an individual who is already showing symptoms. For example, genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of conditions like cystic fibrosis or Huntington's disease.
-
Predictive and Presymptomatic Testing: These tests are for individuals who do not currently show symptoms but are at risk of developing a genetic disorder later in life. For example, BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene tests can indicate an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
-
Carrier Testing: This type of test is often used by couples planning to have children. It helps determine if one or both partners carry a gene for a genetic disorder that could be passed on to their offspring.
-
Pharmacogenomic Testing: This test analyzes how your genes affect your response to certain medications. It can help doctors choose the most effective medication and dosage for you, reducing the risk of adverse drug reactions.
-
Prenatal Testing: Conducted during pregnancy to check for genetic conditions in the developing fetus. For example, amniocentesis can detect Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
-
Newborn Screening: Performed shortly after birth to detect genetic conditions that can be treated early in life. Commonly screened conditions include phenylketonuria (PKU) and congenital hypothyroidism.
-
Ancestry and Genealogy Testing: These tests trace your ancestral roots and provide information about your ethnic background. They are not typically used for health-related purposes but can be combined with other genetic tests for a more comprehensive understanding of your genetics.
How Does Genetic Testing Work?
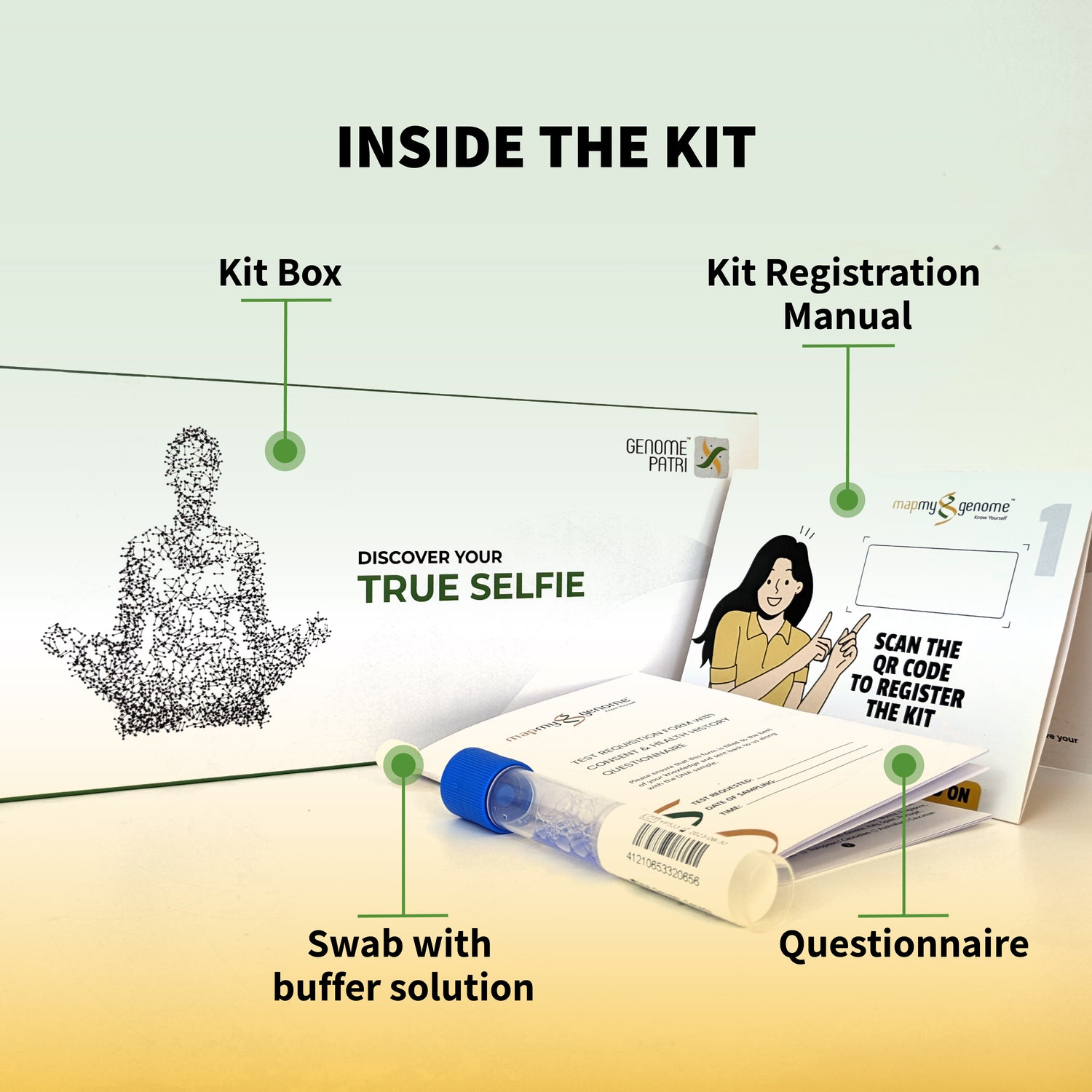
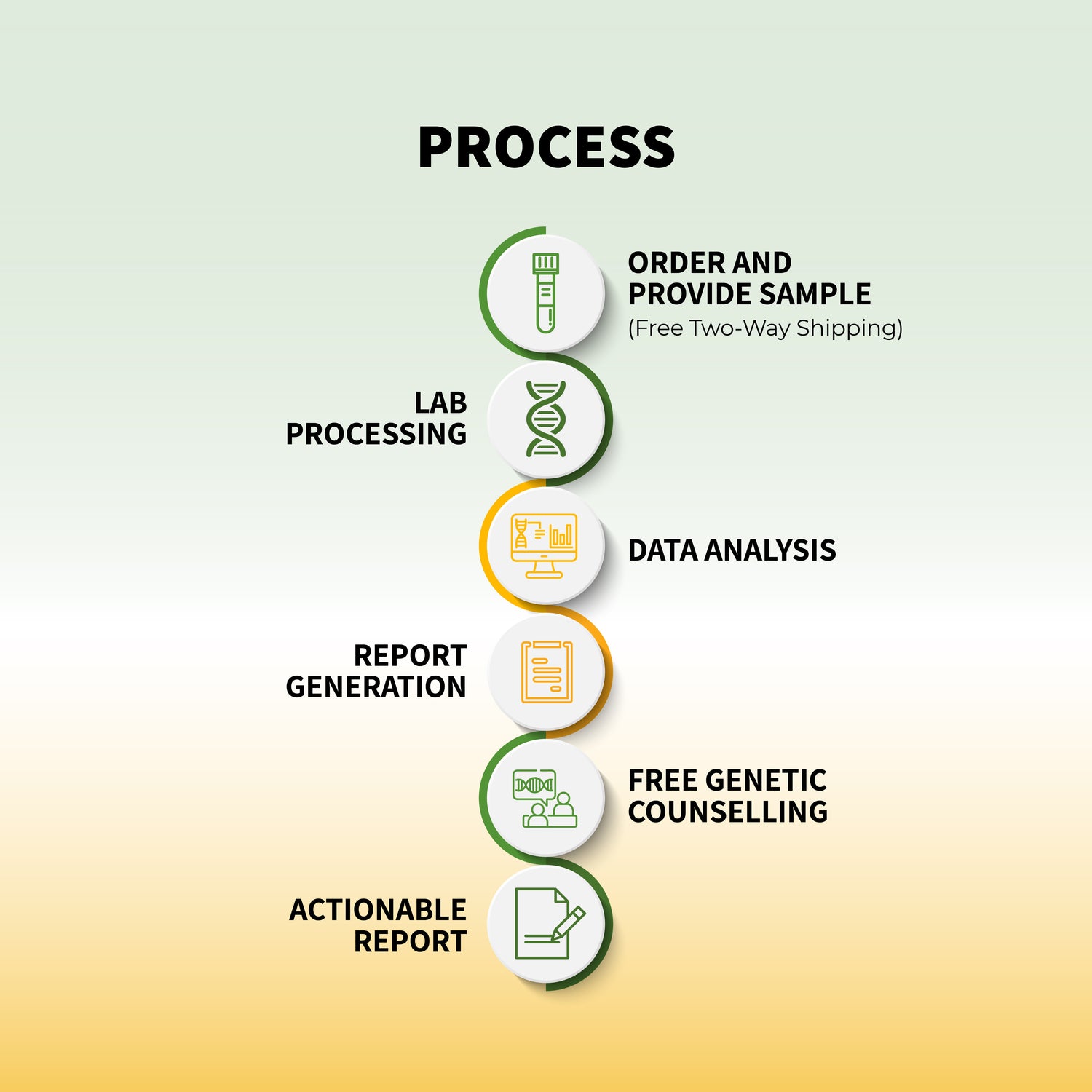
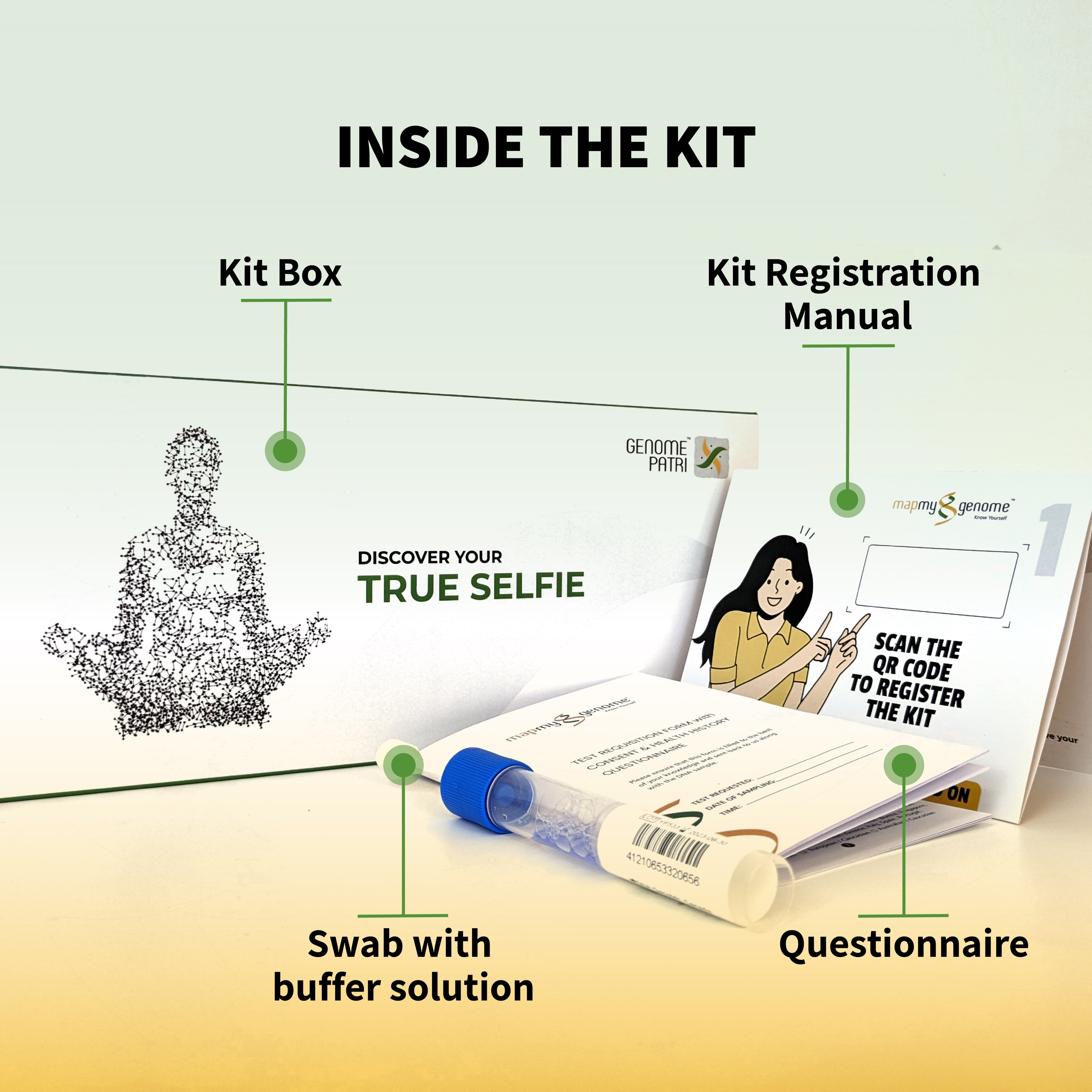
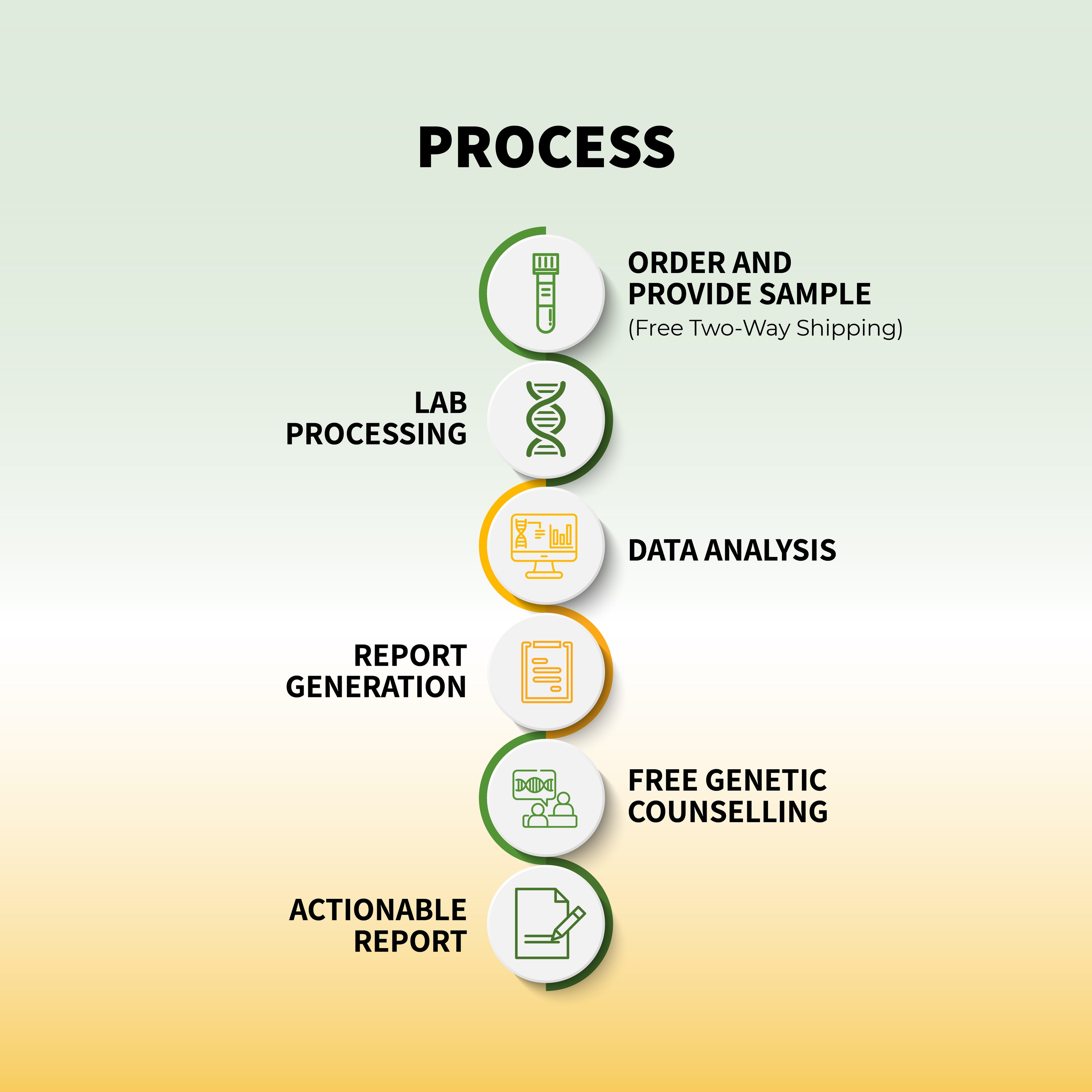
Genetic testing typically involves collecting a sample of your DNA. The most common method is a simple swab of the inside of your cheek, though blood tests, saliva samples, or even skin biopsies can also be used. Once the sample is collected, it is sent to a laboratory where technicians analyze the DNA to look for specific genetic markers associated with certain conditions or traits.
The results of your genetic test are usually returned within a few weeks. Your healthcare provider or a genetic counselor will review the results with you, explaining what they mean and how they might affect your health.
The Importance of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing offers numerous benefits:
-
Early Detection and Prevention: By identifying your genetic predisposition to certain diseases, you can take proactive steps to manage your health. For instance, if you discover that you have a higher risk for a condition like heart disease, you can adopt a healthier lifestyle, monitor your health more closely, and possibly take preventive medications.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Genetic testing provides you with critical information that can guide your health decisions. Whether it's choosing the right medication or making decisions about family planning, knowing your genetic profile empowers you to make more informed choices.
-
Personalized Healthcare: One of the most exciting aspects of genetic testing is its role in personalized medicine. By understanding your unique genetic makeup, healthcare providers can tailor treatments and interventions to your specific needs, leading to more effective and targeted care.
-
Understanding Your Family's Health: Genetic testing can reveal information about conditions that may run in your family. This knowledge can be invaluable for your relatives, as they can take steps to monitor or prevent the same conditions.
-
Reproductive Planning: For couples considering having children, genetic testing can provide insights into potential risks and help guide family planning decisions. Carrier testing, for example, can identify whether you or your partner carry genes for certain inherited disorders.
Who Should Consider Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing is not just for individuals with a family history of genetic disorders. It can be beneficial for a wide range of people, including:
-
Those with a family history of a genetic disorder: If certain conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, or diabetes, are common in your family, genetic testing can help assess your risk.
-
Individuals planning to start a family: Carrier testing can reveal if you or your partner carry genes for inherited conditions that could affect your children.
-
People with a personal history of a genetic condition: If you have already been diagnosed with a genetic disorder, testing can provide more information about your condition and help guide treatment.
-
Anyone interested in personalized medicine: If you want to know how your genetics affect your response to medications or your risk for certain conditions, genetic testing can provide valuable insights.
Ethical Considerations and Privacy
While genetic testing offers many benefits, it's important to consider the ethical implications. Your genetic information is deeply personal, and privacy is a major concern. Fortunately, there are strict regulations in place to protect your genetic data.
Before undergoing genetic testing, it's crucial to discuss the potential risks and benefits with a healthcare provider or genetic counselor. They can help you understand the implications of the test and how the results may impact you and your family.
Conclusion
Genetic testing is a powerful tool that can provide insights into your health, guide personalized treatment, and even help prevent future health issues. Whether you're new to the concept or have been considering it for some time, understanding the basics of genetic testing is the first step toward making informed decisions about your health.
By exploring your genetic makeup, you can gain a deeper understanding of your body and take control of your health in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. As the field of genetics continues to advance, the possibilities for personalized healthcare are only expanding, offering new hope for a healthier future.