Deep within the intricate folds of your brain, a silent symphony of chemical messengers is constantly playing out. These tiny molecules, known as neurotransmitters, are the conductors of your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. From the surge of dopamine that fuels your motivation to the calming embrace of serotonin that promotes relaxation, neurotransmitters are the orchestra that orchestrates the complex dance of your mental and physical well-being.
The Essential Players in the Brain's Chemical Symphony
The brain's chemical symphony features a diverse cast of neurotransmitters, each with its unique role to play. Here are some of the key players:
- Dopamine: The "feel-good" neurotransmitter, dopamine is associated with pleasure, reward, motivation, and focus. It plays a crucial role in learning, memory, and movement.
- Serotonin: The "mood stabilizer," serotonin helps regulate mood, sleep, appetite, and digestion. Low serotonin levels are linked to depression, anxiety, and insomnia.
- GABA: The "calming influence," GABA is the brain's primary inhibitory neurotransmitter. It helps to quiet down nerve activity and promote relaxation.
- Acetylcholine: The "memory maestro," acetylcholine is essential for learning, memory, and muscle movement. It also plays a role in attention and arousal.
- Endorphins: The "natural painkillers," endorphins are released in response to pain, stress, and excitement. They create feelings of euphoria and well-being.
- Norepinephrine: The "alertness activator," norepinephrine helps you stay focused and energized. It also plays a role in the "fight-or-flight" response.
- Oxytocin: The "love hormone," oxytocin is associated with social bonding, trust, and empathy. It is also involved in childbirth, breastfeeding, and sexual arousal.
- Histamine: The "immune system regulator," histamine is involved in the immune system, digestion, and the nervous system. It is also responsible for the symptoms of allergies, such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
- Cortisol: The "stress hormone," cortisol is released in response to stress. It helps to regulate blood sugar levels and can also affect mood, sleep, and appetite.
How Food and Lifestyle Choices Influence Neurotransmitters
The foods you eat and the lifestyle choices you make can significantly impact your neurotransmitter levels. Here are some tips for supporting healthy neurotransmitter function:
- Eat a balanced diet: Choose foods that are rich in nutrients that support brain health, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins.
- Limit processed foods: Processed foods are often high in sugar and unhealthy fats, which can contribute to inflammation and disrupt neurotransmitter function.
- Get regular exercise: Exercise is a great way to boost your mood and improve your cognitive function. It also helps to regulate stress hormones and promote the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and endorphins.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep is essential for brain health and neurotransmitter function. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can disrupt neurotransmitter levels and lead to mental health problems. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Connect with others: Social connection is important for mental and emotional well-being. Spend time with loved ones, join a club or group, or volunteer in your community.
The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Connection
Recent research suggests that the gut microbiome, the trillions of bacteria that live in your gut, may also play a role in neurotransmitter function. A healthy gut microbiome has been linked to improved mood, reduced anxiety, and better cognitive function.
How to Support a Healthy Gut Microbiome
You can support a healthy gut microbiome by eating a diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and probiotics. You can also take probiotics supplements or eat foods that are naturally high in probiotics, such as yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut.
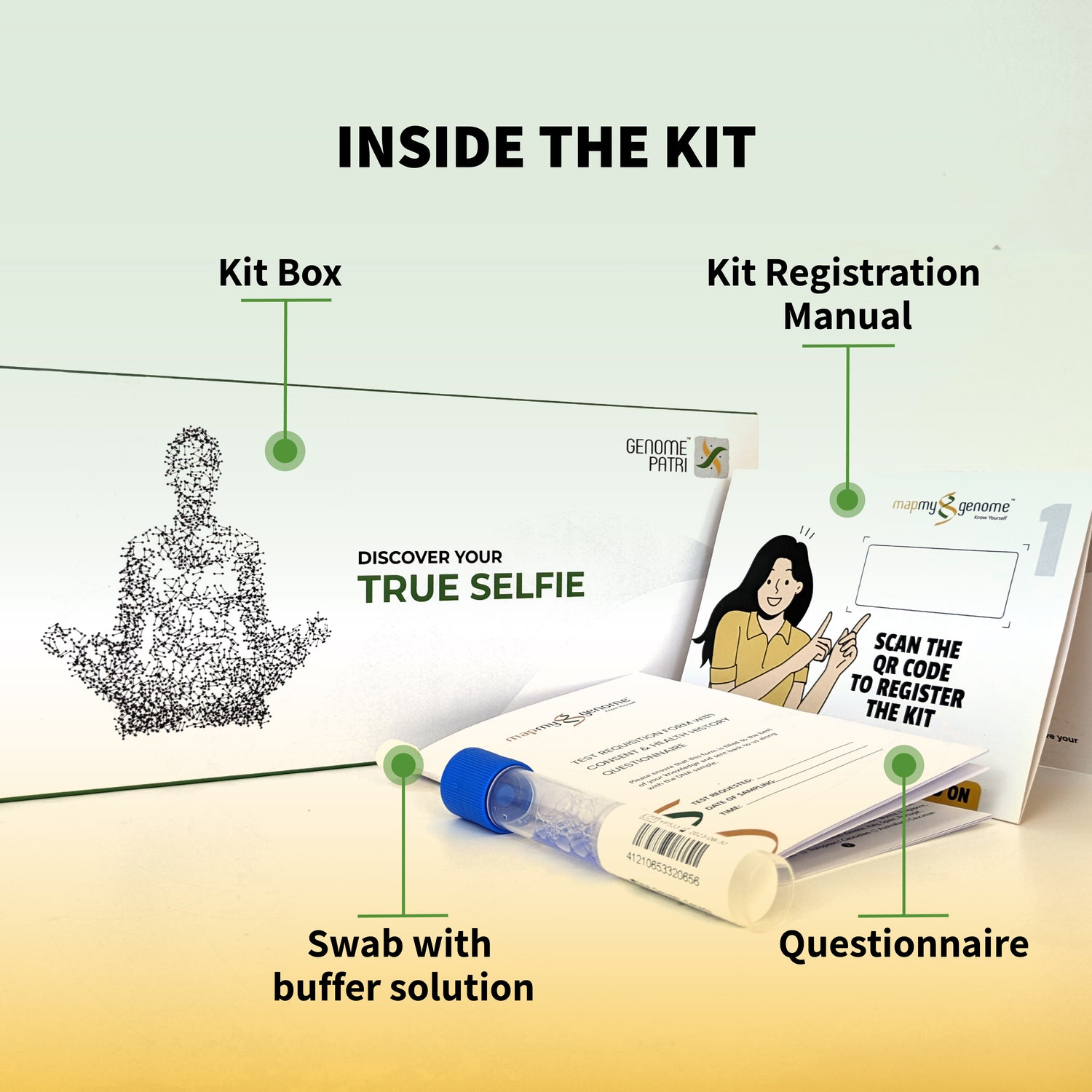
Microbiome and Genetic Testing: Your Personalized Roadmap to Health
In the pursuit of optimal health, personalized approaches are gaining traction. Microbiome and genetic testing offer unique insights into your individual needs, allowing you to tailor your diet, lifestyle, and even supplement choices for maximum benefit.
- Microbiome Testing: By analyzing the composition of your gut microbiome, you can identify potential imbalances and deficiencies that may be impacting your overall health and neurotransmitter production. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about dietary changes, prebiotic and probiotic supplementation, and lifestyle modifications to cultivate a thriving gut ecosystem.
- Genetic Testing: Your genes hold valuable information about your predisposition to certain health conditions and your body's unique response to various nutrients and environmental factors. Genetic testing can reveal insights about your neurotransmitter pathways, stress responses, and nutrient absorption capabilities. This information can empower you to make proactive choices regarding diet, exercise, stress management, and supplementation to optimize your health and prevent future health issues.
Conclusion
Neurotransmitters are the unsung heroes of your brain, playing a vital role in regulating your mood, behavior, and overall health. By understanding how neurotransmitters work and how you can support their function, you can take steps to improve your mental and physical well-being. Moreover, embracing personalized approaches like microbiome and genetic testing can further empower you to make informed decisions about your health, paving the way for a more vibrant and fulfilling life.