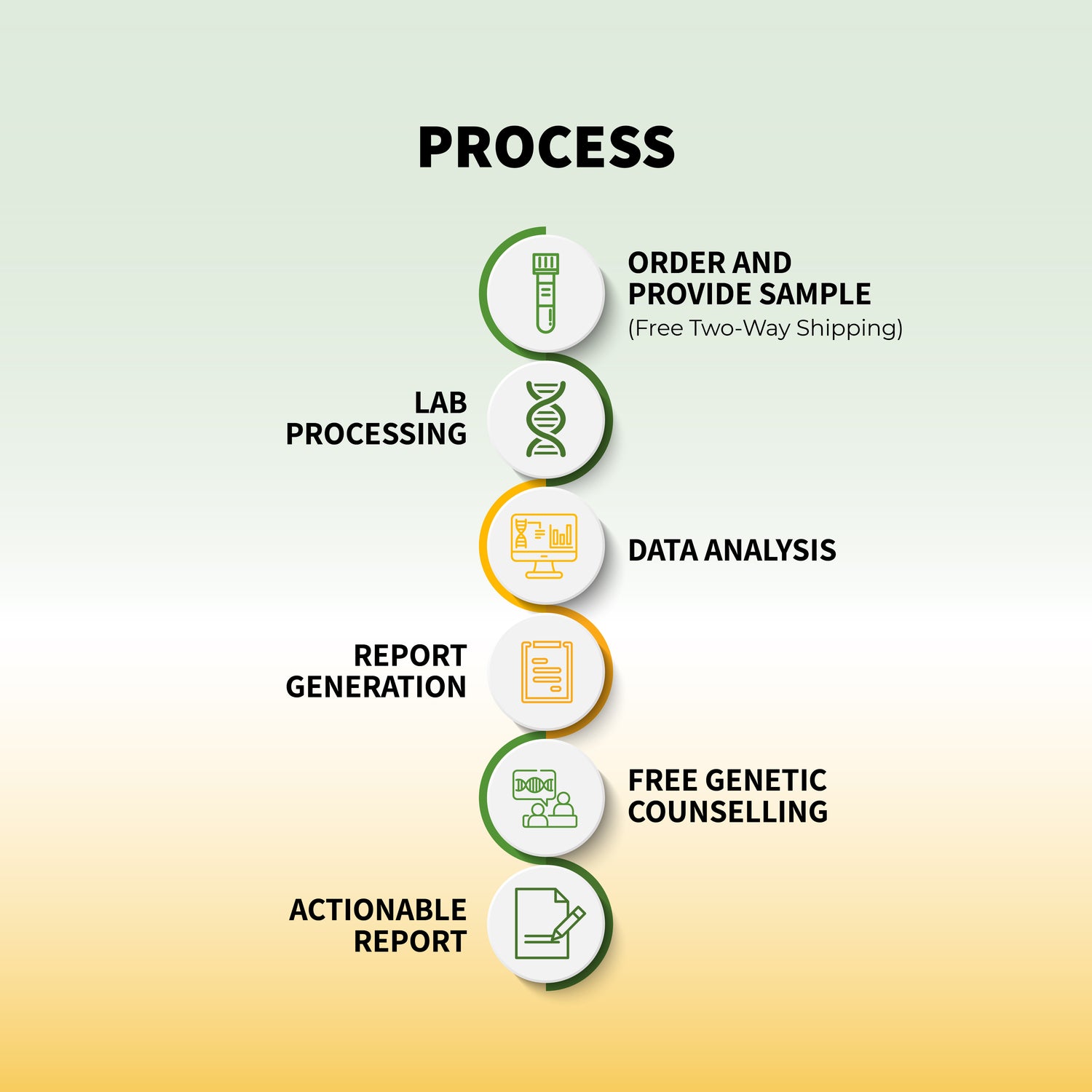
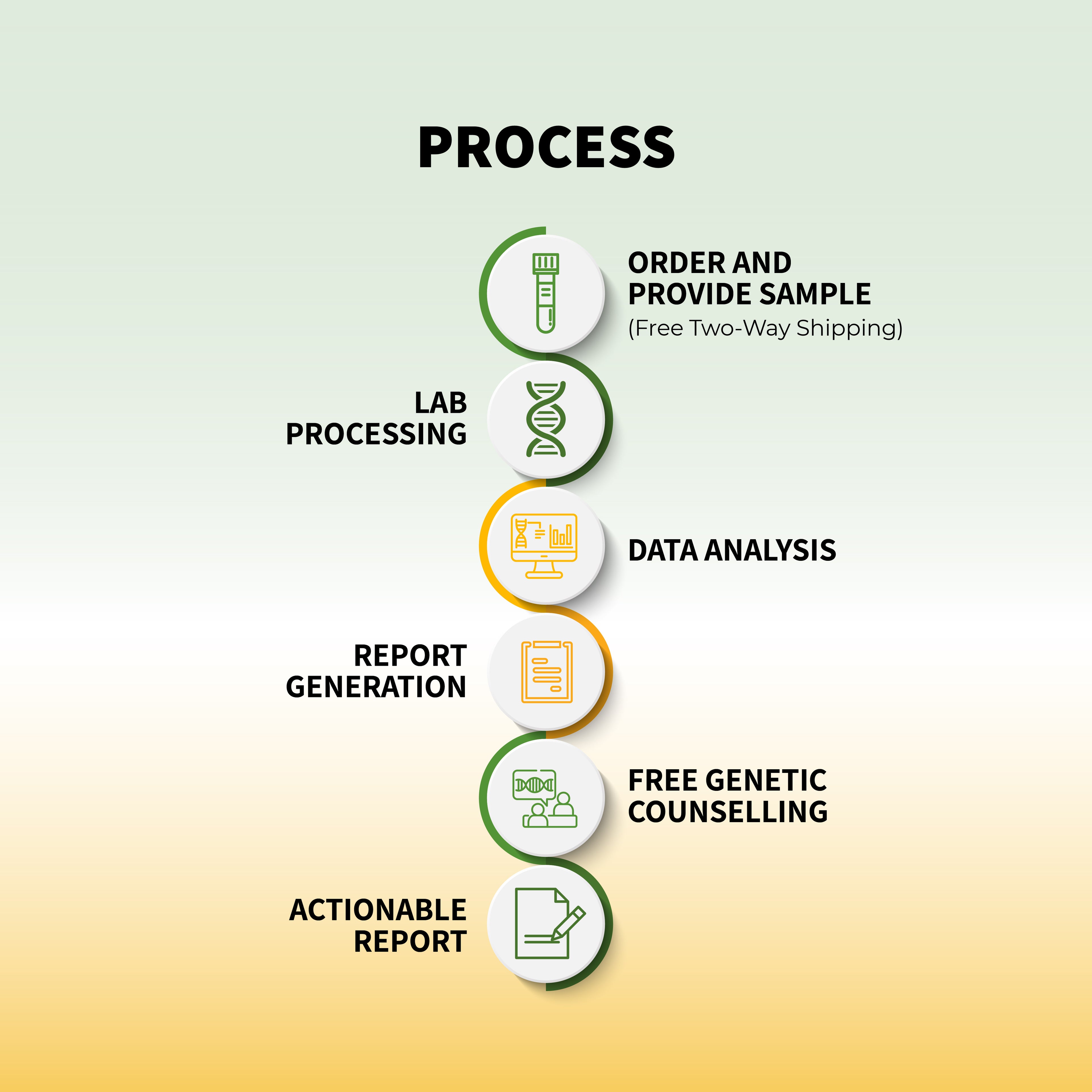
Mental health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, influencing how we think, feel, and behave. While environmental factors and life experiences undoubtedly play significant roles in mental health, an often-overlooked component is the influence of genetics. Recent advancements in genetic research have shed light on how our DNA can predispose us to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. In this blog post, we will explore the link between genetics and mental health, and how genetic testing can be a powerful tool for managing these conditions.
Understanding Genetic Predisposition to Mental Illness
The idea that mental health disorders can run in families is not new. For years, researchers have observed that conditions like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia often affect multiple members of the same family. This observation led to the hypothesis that genetics could play a role in the development of these conditions.
-
What is Genetic Predisposition?
Genetic predisposition refers to the increased likelihood of developing a particular condition based on one's genetic makeup. It does not mean that a person will definitely develop the condition, but rather that they have a higher risk compared to someone without the same genetic variants. -
Polygenic Nature of Mental Health Disorders:
Mental health conditions are often polygenic, meaning they are influenced by multiple genes rather than a single gene mutation. These genes can affect neurotransmitter function, brain structure, and stress response, all of which contribute to mental health. For instance, certain genetic variants are associated with how the brain processes serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in mood regulation. People with these variants may be more susceptible to depression, especially when combined with environmental stressors. -
The Role of Epigenetics:
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence. Environmental factors such as stress, trauma, and even diet can trigger these changes, activating or deactivating certain genes that influence mental health. This means that while genetics can predispose someone to mental illness, lifestyle and environmental factors can determine whether these genetic tendencies manifest as a disorder.
The Impact of Genetics on Specific Mental Health Disorders
-
Depression:
Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide. Research has identified several genetic variants associated with depression, many of which are involved in the regulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. While having these genetic variants does not guarantee that a person will develop depression, it increases their vulnerability, particularly if they experience significant life stressors or trauma. -
Anxiety Disorders:
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, have also been linked to genetic factors. Studies have shown that people with a family history of anxiety disorders are more likely to develop similar conditions. Genes involved in the regulation of the amygdala, the brain's fear center, play a key role in anxiety. Variants in these genes can make an individual more prone to exaggerated fear responses, contributing to the development of anxiety disorders. -
Bipolar Disorder:
Bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings, including episodes of mania and depression. Genetic research has identified several genes associated with bipolar disorder, many of which are involved in the regulation of neurotransmitter systems and circadian rhythms. While the exact cause of bipolar disorder is not fully understood, it is clear that genetics play a significant role in its development. -
Schizophrenia:
Schizophrenia is a severe mental health disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It is highly heritable, with genetics accounting for about 80% of the risk. Researchers have identified multiple genetic variants associated with schizophrenia, many of which are involved in brain development and neurotransmitter regulation. These findings have provided valuable insights into the biological mechanisms underlying the disorder, paving the way for more targeted treatments.
The Role of Genetic Testing in Mental Health Management
As our understanding of the genetic basis of mental health disorders has grown, so too has the potential for using genetic testing as a tool for managing these conditions. While genetic testing cannot predict mental illness with certainty, it can provide valuable information that can help individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about prevention and treatment.
-
Personalized Treatment Plans:
One of the most promising applications of genetic testing in mental health is the development of personalized treatment plans. By understanding a person’s genetic predisposition to certain mental health conditions, healthcare providers can tailor treatment strategies to the individual. For example, genetic testing can identify how a person metabolizes certain medications, helping doctors choose the most effective treatment with the fewest side effects. -
Early Intervention and Prevention:
For individuals with a strong family history of mental health disorders, genetic testing can be a proactive tool for early intervention and prevention. By identifying genetic risk factors early, individuals can take steps to mitigate their risk, such as engaging in regular mental health check-ups, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This proactive approach can help prevent the onset of mental illness or reduce the severity of symptoms if a disorder does develop. -
Reducing Stigma:
Mental health disorders are often stigmatized, leading to shame and reluctance to seek help. By highlighting the biological basis of these conditions, genetic testing can help reduce stigma and promote a more compassionate understanding of mental illness. When people recognize that mental health disorders are influenced by genetics, they may be more likely to seek help and less likely to view these conditions as a personal failing. -
Family Planning:
For couples with a family history of severe mental health disorders, genetic testing can play a role in family planning. By understanding their genetic risks, couples can make informed decisions about having children and explore options such as genetic counseling to assess the likelihood of passing on genetic predispositions to their offspring.
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
While the potential benefits of genetic testing for mental health are significant, there are also important ethical considerations and limitations to keep in mind.
-
Privacy Concerns:
Genetic information is highly personal, and there are concerns about how this information might be used or shared. It's crucial that individuals undergoing genetic testing have a clear understanding of how their data will be stored and protected. -
Genetic Determinism:
There is a risk that genetic testing could lead to genetic determinism, where individuals believe that their genetic makeup entirely dictates their mental health outcomes. It's important to emphasize that genetics is just one piece of the puzzle, and environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and therapeutic interventions all play crucial roles in mental health. -
Access and Cost:
Access to genetic testing is not universal, and cost can be a barrier for many people. Ensuring that genetic testing and associated counseling are accessible and affordable is essential for maximizing the benefits of these advancements in mental health care.
Conclusion: A New Era in Mental Health Care
The connection between genetics and mental health disorders is a rapidly evolving field of study, offering new insights into the biological underpinnings of conditions like depression and anxiety. As genetic testing becomes more integrated into mental health care, it holds the promise of personalized treatment plans, early intervention, and a deeper understanding of the factors that contribute to mental illness.
If you have a family history of mental health disorders or are struggling with your mental health, consider discussing the potential benefits of genetic testing with your healthcare provider. While it’s not a definitive predictor of mental illness, genetic testing can provide valuable information that may help you better manage your mental health and make informed decisions about your care.
By embracing the role of genetics in mental health, we can move toward a more personalized and compassionate approach to mental health care, helping individuals live healthier, more fulfilling lives.