Food allergies and sensitivities affect millions of people worldwide, leading to uncomfortable and potentially dangerous reactions. But what if the key to understanding these reactions lies within your DNA? Recent advancements in genetic testing have made it possible to identify food allergies and sensitivities through personalized DNA analysis. In this blog, we'll explore the role of genetics in food allergies and how DNA testing can help you understand and manage your body’s reactions to certain foods.
Understanding Food Allergies
A food allergy occurs when your immune system mistakenly identifies a particular food protein as harmful and triggers an immune response. This response can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild reactions like hives or itching to more severe symptoms like anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening. Common food allergens include peanuts, shellfish, milk, and eggs, but any food can potentially trigger an allergic reaction.
While food allergies are typically diagnosed through skin prick tests or blood tests, these traditional methods can sometimes be inconclusive or miss specific sensitivities. This is where genetic testing steps in to offer a more precise and personalized approach.
The Genetics Behind Food Allergies
Food allergies are often linked to genetic factors. If you have a family history of allergies or other immune-related conditions, your risk of developing food allergies is significantly higher. Certain genes are known to influence immune system responses, and mutations or variations in these genes can make you more susceptible to food allergies.
One of the key genes involved is the HLA gene family (Human Leukocyte Antigen), which plays a crucial role in how your immune system recognizes foreign substances. Variations in these genes can increase your likelihood of developing allergies, including those to food. In addition, genes that regulate immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels – a type of antibody involved in allergic reactions – can also influence your body’s reaction to certain allergens.
How DNA Testing Can Identify Food Allergies
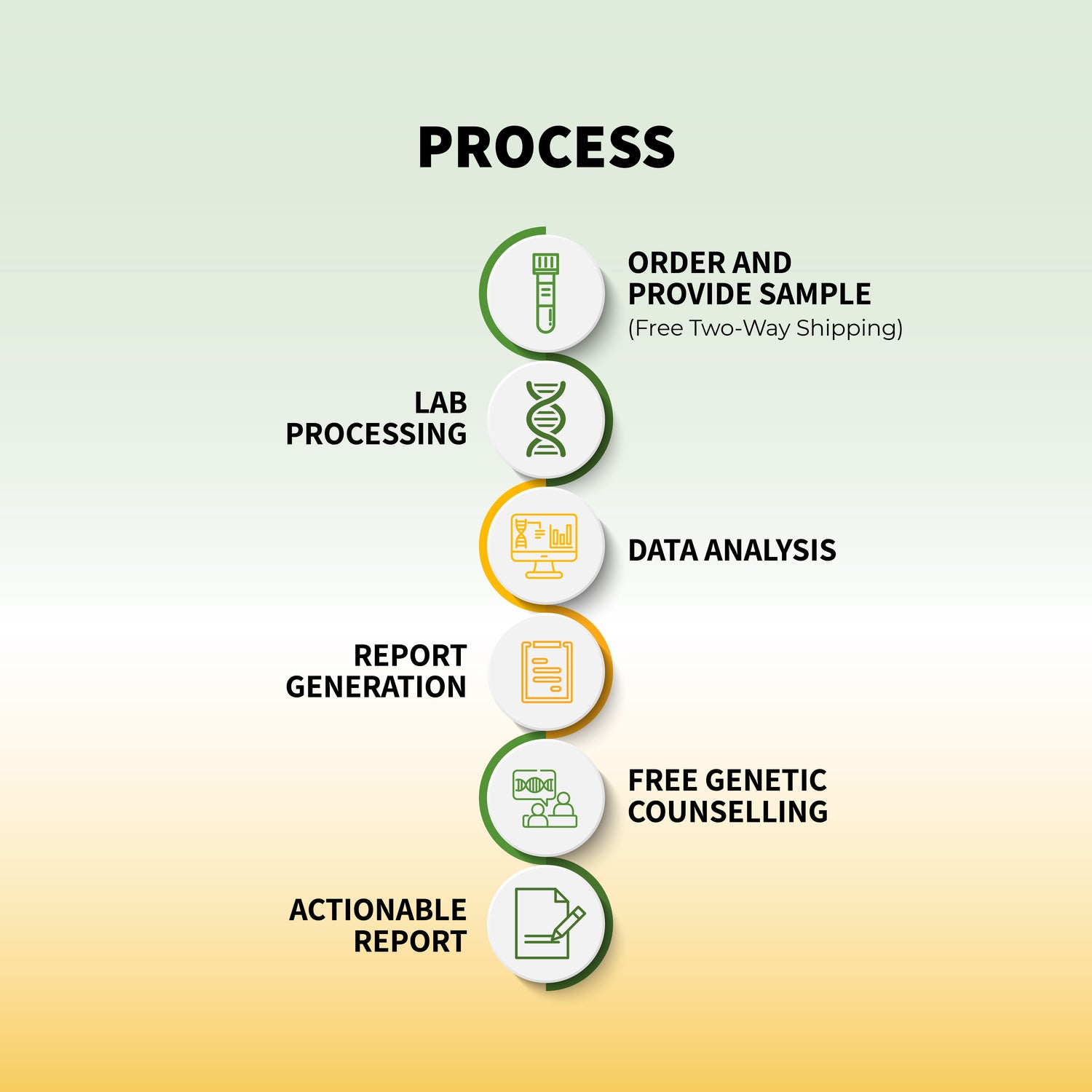
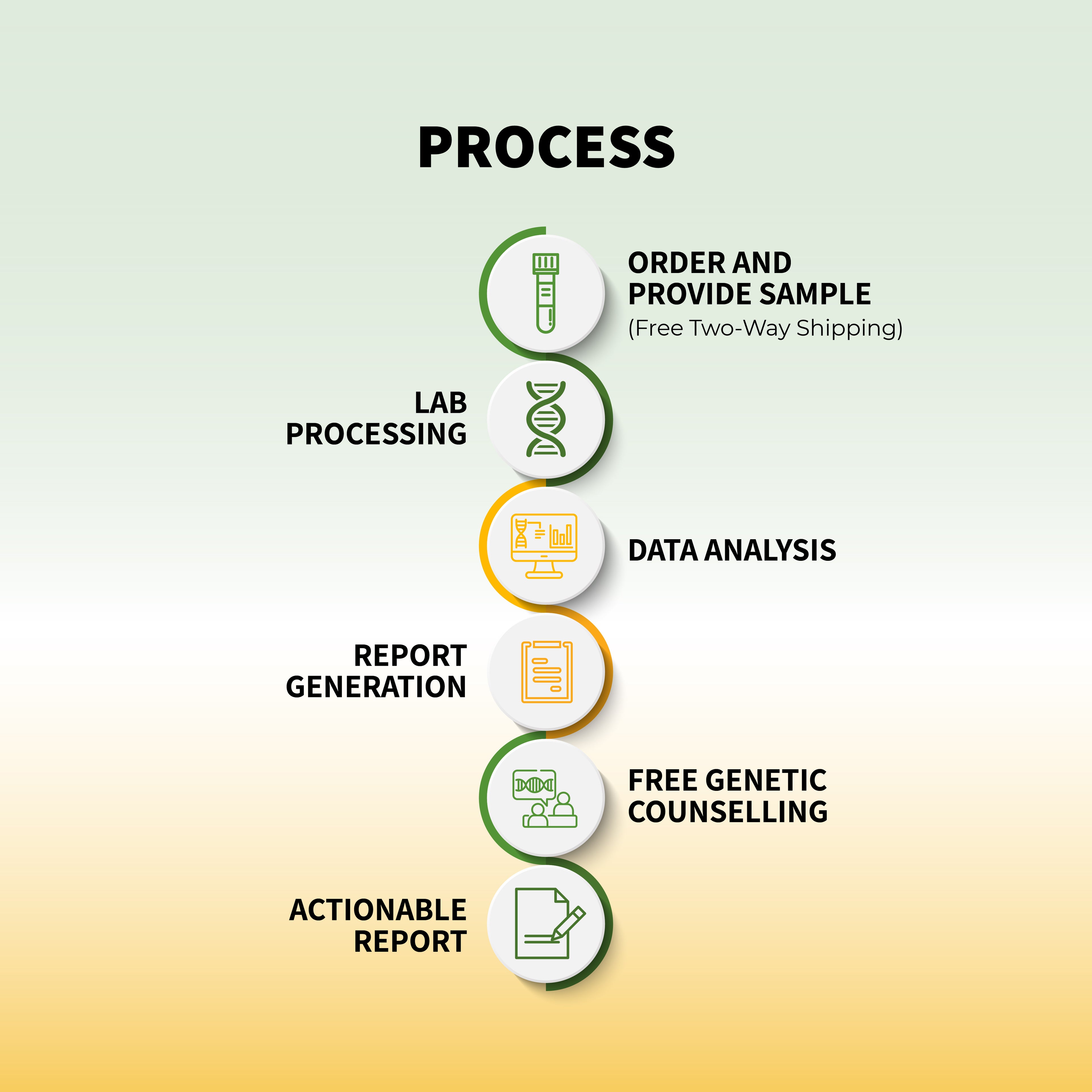
DNA testing for food allergies focuses on identifying specific genetic markers associated with increased sensitivity to allergens. A simple saliva or blood sample can be analyzed to detect variations in genes related to the immune response. By examining these genetic factors, DNA tests can reveal your predisposition to certain food allergies and sensitivities.
Here’s how genetic testing for food allergies works:
-
Comprehensive Analysis: The test looks for genetic variations that increase the risk of developing food allergies. This includes examining the HLA gene family and IgE-related genes, which are associated with allergic responses.
-
Identification of Risk Factors: DNA tests can identify whether you have inherited genetic variants that make you more susceptible to food allergies. This information can be crucial for early prevention and management.
-
Personalized Insights: Once your genetic information is analyzed, you'll receive a detailed report outlining which foods you're more likely to be allergic to and the severity of potential reactions. This can help you make informed dietary choices and avoid harmful allergens.
Genetic Testing vs. Traditional Food Allergy Testing
Traditional food allergy testing methods, such as skin prick tests and blood tests, are widely used to diagnose allergies, but they have limitations. These tests measure your body’s immediate response to allergens, but they may not capture underlying sensitivities that don’t trigger immediate symptoms. Additionally, they might not reveal whether you have a genetic predisposition to certain allergies that haven’t yet developed.
In contrast, genetic testing offers a deeper understanding of your body's potential allergic responses. By identifying genetic markers linked to food allergies, you can gain insights into your long-term risk of developing allergies, even if you're not currently experiencing symptoms. This information can empower you to take proactive steps to manage your health.
Can DNA Testing Help With Food Intolerances?
While food allergies involve an immune system response, food intolerances are related to your body’s inability to properly digest certain foods. A common example is lactose intolerance, which occurs when your body lacks the enzyme needed to break down lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Food intolerances can lead to uncomfortable digestive symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Genetic testing can also help identify food intolerances by analyzing genes responsible for enzyme production. For example, a DNA-based dairy intolerance test can reveal whether you have genetic variations that affect your ability to digest lactose. This can help you understand whether symptoms like stomach discomfort after consuming dairy are due to lactose intolerance rather than an allergic reaction.
The Benefits of DNA-Based Allergy Testing
-
Precision and Personalization: Unlike traditional allergy tests, genetic testing provides precise insights based on your unique genetic makeup. This personalized approach ensures that you get specific recommendations tailored to your body’s needs.
-
Early Detection and Prevention: If you have a family history of allergies, genetic testing can help detect your risk early, allowing you to take preventive measures to avoid potential allergens and minimize the chances of developing severe allergies in the future.
-
Improved Management of Existing Allergies: If you already have diagnosed food allergies, DNA testing can help you better understand the underlying genetic factors contributing to your condition. This knowledge can guide more effective management strategies, including dietary adjustments.
-
Identification of Hidden Sensitivities: Genetic testing can identify food sensitivities that may not cause immediate allergic reactions but could lead to long-term health issues, such as inflammation or digestive problems. By identifying these sensitivities, you can make better dietary choices and avoid foods that may be harmful to your health.
Steps to Take After Genetic Testing for Food Allergies
Once you've received your genetic testing results, it’s important to take actionable steps to manage your food allergies or sensitivities:
-
Consult a Healthcare Provider: Share your genetic testing results with an allergist or healthcare provider who can help interpret the findings and create a personalized plan to manage your allergies.
-
Adjust Your Diet: Based on your genetic results, modify your diet to avoid allergens and foods you're sensitive to. For example, if your results indicate a risk for dairy intolerance, you may want to reduce or eliminate dairy products from your diet.
-
Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of any allergic reactions or symptoms you experience after consuming certain foods. This will help you refine your diet and make informed choices based on your genetic predisposition.
-
Stay Informed: As research on genetics and food allergies continues to evolve, stay updated on the latest findings that may provide additional insights into managing your allergies.
Conclusion
Food allergies can have a significant impact on your daily life, but understanding the role of genetics can empower you to take control of your health.