Diabetes is a chronic condition that impacts millions globally, with its prevalence rising steadily. Recognizing how diabetes symptoms manifest across different age groups is vital for early detection and effective management. In this guide, we will explore how diabetes symptoms vary with age and how genetic testing can offer personalized insights into managing this condition.
Diabetes in Children and Adolescents
Symptoms and Challenges
Diabetes in children and adolescents, particularly Type 1 diabetes, presents unique challenges. Early detection is essential to prevent complications and ensure a better quality of life. Common symptoms include:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: Excess glucose in the bloodstream leads to increased thirst and frequent urination.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite eating more, children with diabetes often lose weight as their bodies cannot use glucose effectively.
- Fatigue: Insufficient glucose in cells results in constant tiredness and lack of energy.
- Irritability and Mood Swings: Fluctuating blood sugar levels can cause emotional instability.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the shape of the eye's lens, leading to vision problems.
Genetic Insights
Genetic testing, such as Genomepatri, can identify predispositions to Type 1 diabetes by analyzing specific gene variants. Early genetic screening can help families manage and monitor potential risks, allowing for timely interventions and personalized care plans.
Diabetes in Young Adults
Symptoms and Challenges
Young adults are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes, although Type 1 diabetes can also occur. Symptoms are often subtle and can be mistaken for other conditions. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Infections: High blood sugar levels can impair the immune system, leading to frequent infections.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: Poor blood circulation and nerve damage can slow down the healing process.
- Darkened Skin Patches: Acanthosis nigricans, a condition where skin darkens and thickens, often appears on the neck and armpits.
- Weight Gain: Insulin resistance can lead to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen.
- Tingling and Numbness: Nerve damage (neuropathy) can cause tingling and numbness in the hands and feet.
Diabetes in Middle-Aged Adults
Symptoms and Challenges
Middle-aged adults are at higher risk for Type 2 diabetes, often linked to lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress. Symptoms include:
- Increased Hunger: Despite eating more, middle-aged adults with diabetes may feel constantly hungry.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent tiredness can interfere with daily activities and work performance.
- Blurred Vision: Changes in blood sugar levels can affect vision, making daily tasks difficult.
- Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels lead to increased urination, particularly at night.
- Heart Disease: Diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular problems, including heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes in Older Adults
Symptoms and Challenges
Older adults face unique challenges in managing diabetes, as the condition can exacerbate age-related health issues. Symptoms include:
- Confusion and Memory Loss: Fluctuating blood sugar levels can impact cognitive function, leading to confusion and memory issues.
- Vision Problems: Diabetic retinopathy, a condition affecting the blood vessels in the retina, can cause significant vision loss.
- Kidney Damage: Diabetes can lead to nephropathy, impairing kidney function and leading to chronic kidney disease.
- Foot Problems: Poor circulation and nerve damage increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Older adults with diabetes are at higher risk for heart disease and strokes.
The Role of Genetic Testing in Diabetes Management
Personalized Health Plans
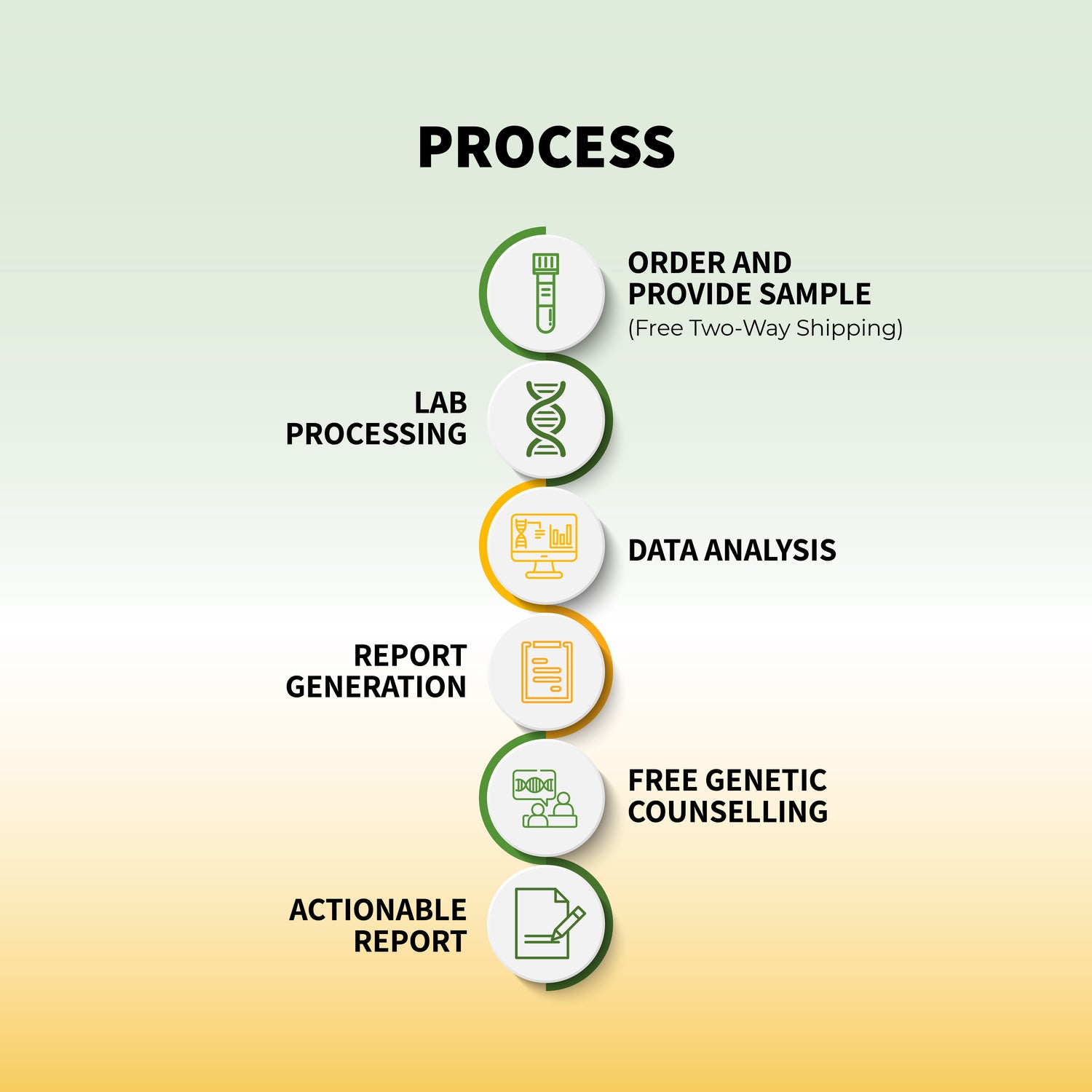
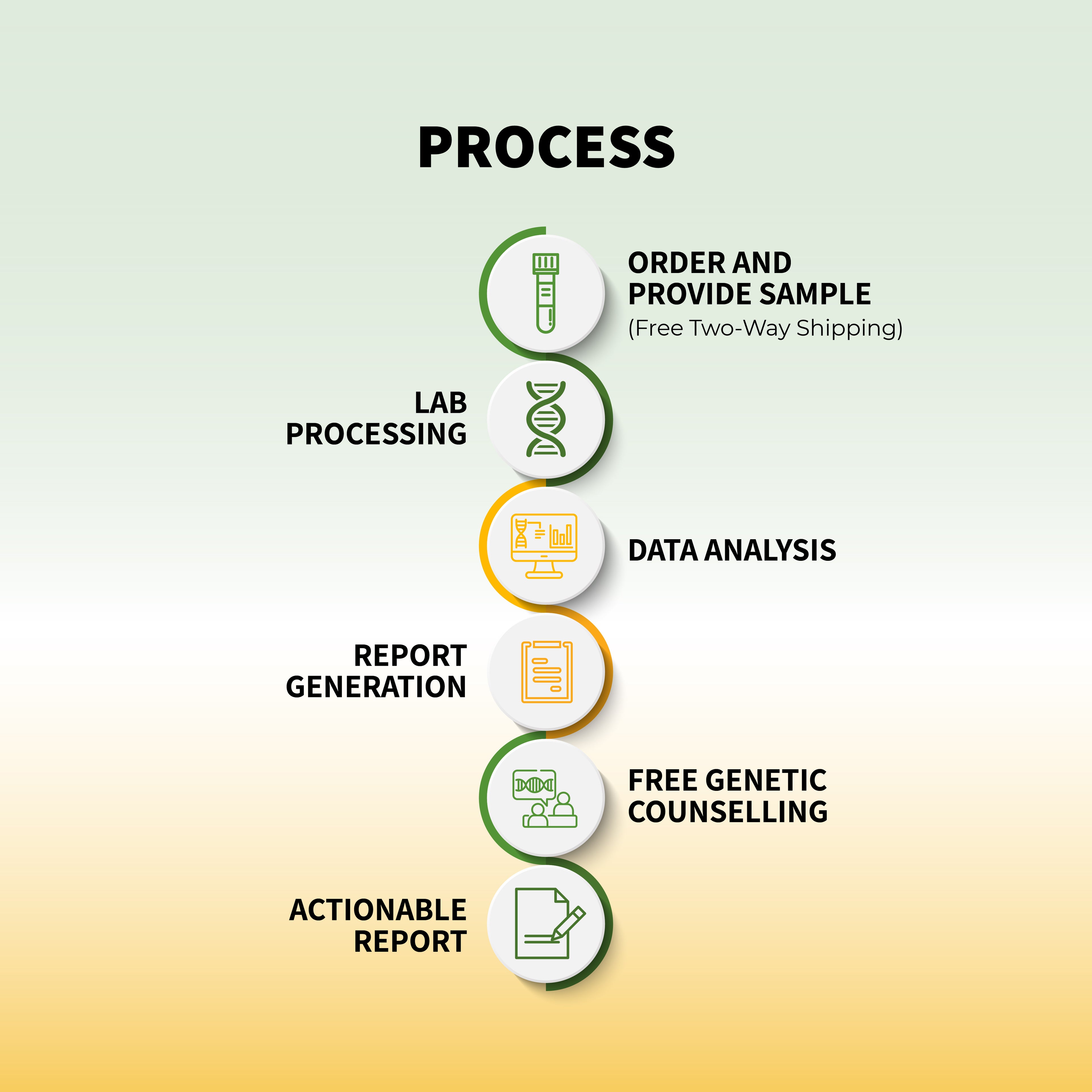
Genetic testing through services like Genomepatri can help individuals understand their unique genetic makeup and how it influences their risk of developing diabetes. This information allows for the creation of personalized health plans that include:
- Tailored Diet Plans: Based on genetic insights, individuals can adopt diets that help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Customized Exercise Regimens: Personalized fitness plans can improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
- Proactive Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and other health markers can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Early Detection and Prevention
Genetic testing can identify individuals at risk of developing diabetes before symptoms appear. Early detection allows for timely interventions, such as lifestyle modifications and regular health screenings, to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes.
Case Study: Managing Diabetes with Genetic Insights
Consider the case of Anita, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. Genetic testing revealed specific gene variants associated with insulin resistance. Armed with this information, Anita worked with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that included a low-glycemic diet, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques. Over time, Anita's blood sugar levels stabilized, and she experienced fewer diabetes-related complications.
Conclusion
Understanding how diabetes symptoms change with age and leveraging genetic testing for personalized insights can significantly improve diabetes management. Whether you are a parent concerned about your child's risk, a young adult looking to stay healthy, or an older adult managing multiple health issues, genetic testing can provide valuable information to guide your health journey.
By staying informed and proactive, you can take control of your diabetes and live a healthier, more fulfilling life. Explore the benefits of genetic testing with MapmyGenome and unlock the potential of personalized health management today.