Cancer is one of the leading causes of death globally, with millions of new cases diagnosed every year. While lifestyle factors and environmental exposure are significant contributors to cancer risk, genetics also play a crucial role. Genetic mutations passed down from generation to generation can increase the likelihood of developing cancer.
Genetic testing for cancer is a powerful tool that helps in identifying individuals who may have a higher risk of developing specific types of cancer. By understanding your genetic predisposition, you can take proactive steps towards cancer prevention, early detection, and even personalized treatment.
What is Genetic Testing for Cancer?
Genetic testing for cancer involves analyzing a person’s DNA to look for inherited mutations in specific genes known to increase the risk of cancer. It can be used for several types of cancers, including breast cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and more.
Some of the well-known genes associated with cancer include:
- BRCA1 and BRCA2: Mutations in these genes are linked to an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
- MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2: Mutations in these genes are associated with Lynch syndrome, which increases the risk of colorectal and other cancers.
Genetic testing can help assess the risk for hereditary cancer syndromes, where a specific mutation significantly increases the chances of developing certain cancers.
How Does Genetic Testing for Cancer Work?
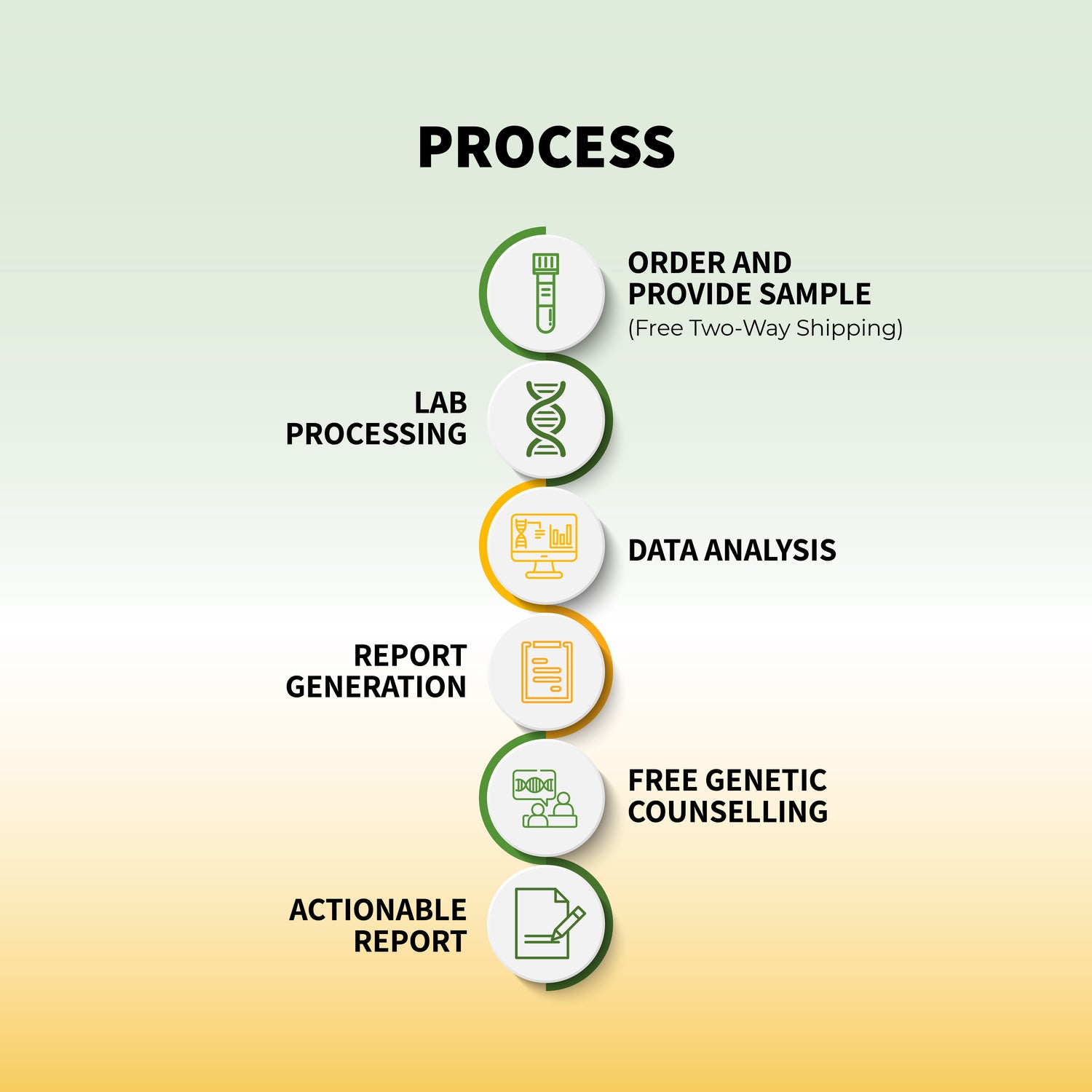
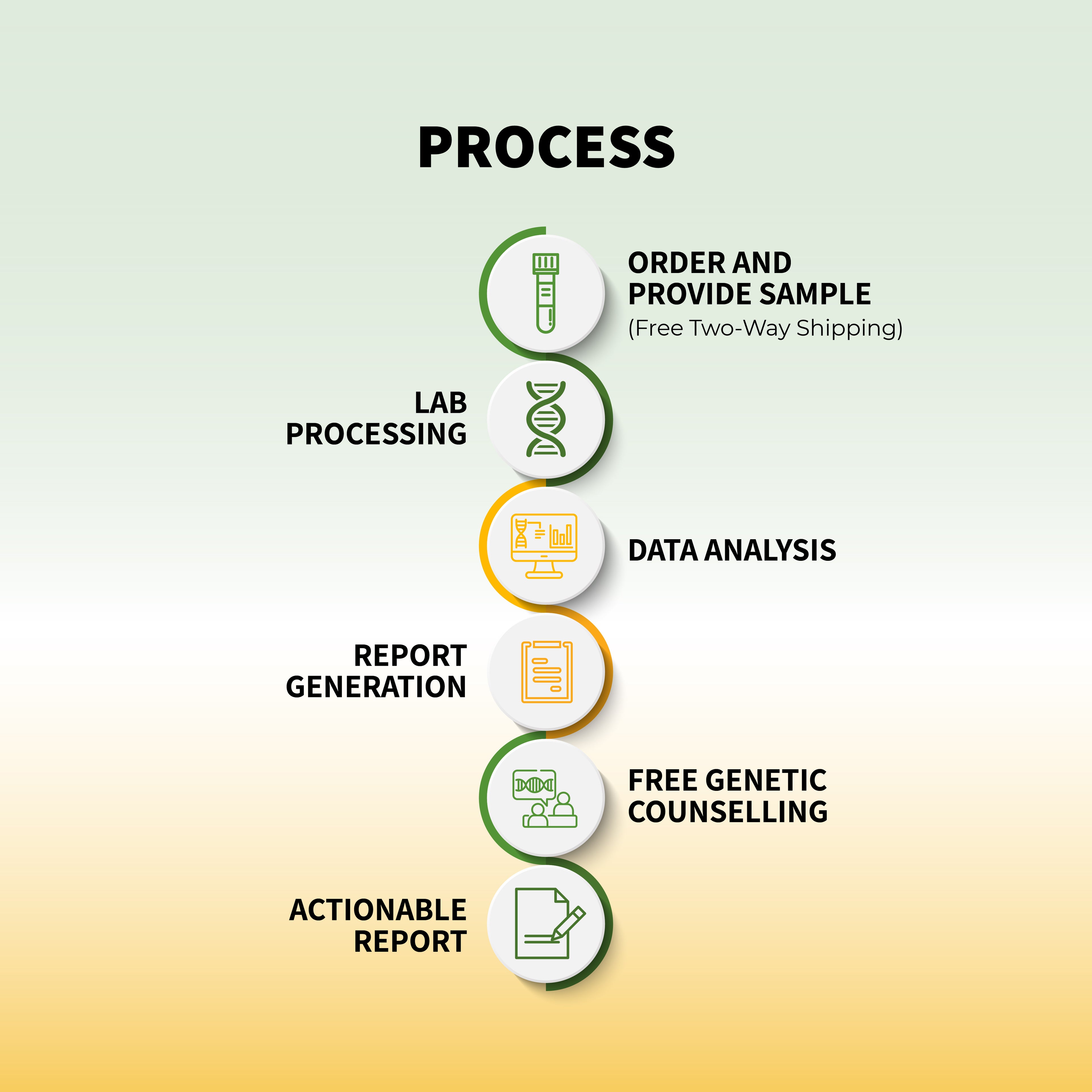
The genetic testing process is relatively simple:
- Consultation: Before getting tested, you usually meet with a healthcare provider or genetic counselor. They’ll review your family and medical history to determine whether genetic testing is appropriate for you.
- Sample Collection: Genetic testing typically requires a sample of your saliva or blood. In some cases, tissue samples might be collected from the tumor if the cancer is already diagnosed.
- Laboratory Testing: The sample is sent to a laboratory, where scientists analyze the DNA to look for any mutations that may be linked to cancer.
- Results Interpretation: Once the test is complete, a genetic counselor or healthcare provider will discuss the results with you. They will explain what the findings mean for your cancer risk and what actions you can take moving forward.
Why Should You Consider Genetic Testing for Cancer?
-
Identifying High-Risk Individuals Genetic testing can help identify individuals who have a higher risk of developing certain cancers due to inherited mutations. If you have a strong family history of cancer, genetic testing can provide valuable insights into your genetic predisposition.
-
Early Detection If a genetic mutation is identified, individuals can undergo more frequent screenings, such as mammograms or colonoscopies, to detect cancer at an early stage when treatment is more effective.
-
Personalized Prevention Plans Armed with the knowledge of your genetic risk, you can take proactive steps to reduce your chances of developing cancer. This may include lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise. In some cases, doctors may recommend preventive surgeries or medications to lower your risk.
-
Family Planning Genetic testing for cancer can also help guide family planning decisions. If you have a hereditary cancer mutation, you may want to discuss options like preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) or IVF with a genetic counselor.
-
Personalized Treatment Options For individuals who have already been diagnosed with cancer, genetic testing can guide treatment decisions. Many cancers, such as breast, ovarian, and lung cancers, have specific genetic mutations that influence how the cancer behaves and responds to treatment. Targeted therapies can be tailored to address the mutations identified through genetic testing.
Who Should Consider Genetic Testing for Cancer?
Genetic testing isn’t recommended for everyone. It’s typically suggested for individuals with:
- A personal or family history of cancer diagnosed at an early age (e.g., breast cancer before age 50)
- Multiple family members with the same or related types of cancer
- A family member with a known genetic mutation associated with cancer
- A history of multiple types of cancer in the same individual
- Certain types of cancer that are known to be hereditary, such as ovarian cancer or male breast cancer
Types of Genetic Tests for Cancer
There are several types of genetic tests available for cancer risk assessment:
-
Single-Gene Testing: This type of test looks for mutations in a specific gene, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, based on an individual’s family history or type of cancer.
-
Panel Testing: Panel testing involves analyzing multiple genes at once to look for mutations that could increase cancer risk. It’s often used when there is a strong family history of different types of cancers.
-
Tumor Profiling (Somatic Testing): Unlike hereditary genetic testing, which looks for inherited mutations, tumor profiling examines the genetic changes in a cancerous tumor. This can help identify targeted therapies or clinical trial options.
Limitations of Genetic Testing for Cancer
While genetic testing can provide valuable insights, it’s important to understand its limitations:
- Not All Cancers Are Genetic: Most cancers are caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. A negative result from genetic testing doesn’t mean you won’t develop cancer, just that you don’t carry a specific inherited mutation.
- Variants of Uncertain Significance: Sometimes genetic testing may find a mutation, but it’s unclear whether that mutation increases cancer risk. This is called a “variant of uncertain significance” (VUS), and it can make decision-making more complex.
- Psychological Impact: Learning about your genetic risk for cancer can be emotionally challenging. It’s important to have access to genetic counseling to help navigate the results and any associated stress or anxiety.
The Role of Genetic Counselors
Genetic counselors play a crucial role in the genetic testing process. They help individuals understand the benefits and risks of testing, interpret test results, and provide support for making informed decisions about cancer prevention, screening, and treatment.
Genetic Testing for Cancer in India
In India, genetic testing for cancer is becoming more accessible, with several healthcare providers, laboratories, and hospitals offering these services. Major platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, and Tata 1mg even provide home testing kits for easier access to genetic insights.
Conclusion
Genetic testing for cancer is a powerful tool that can help identify individuals at risk of developing certain cancers, guide personalized treatment plans, and empower individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention and early detection. If you have a family history of cancer or are concerned about your cancer risk, consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether genetic testing is appropriate for you.
Taking control of your health through genetic insights could be the key to early intervention and improved outcomes in the fight against cancer.