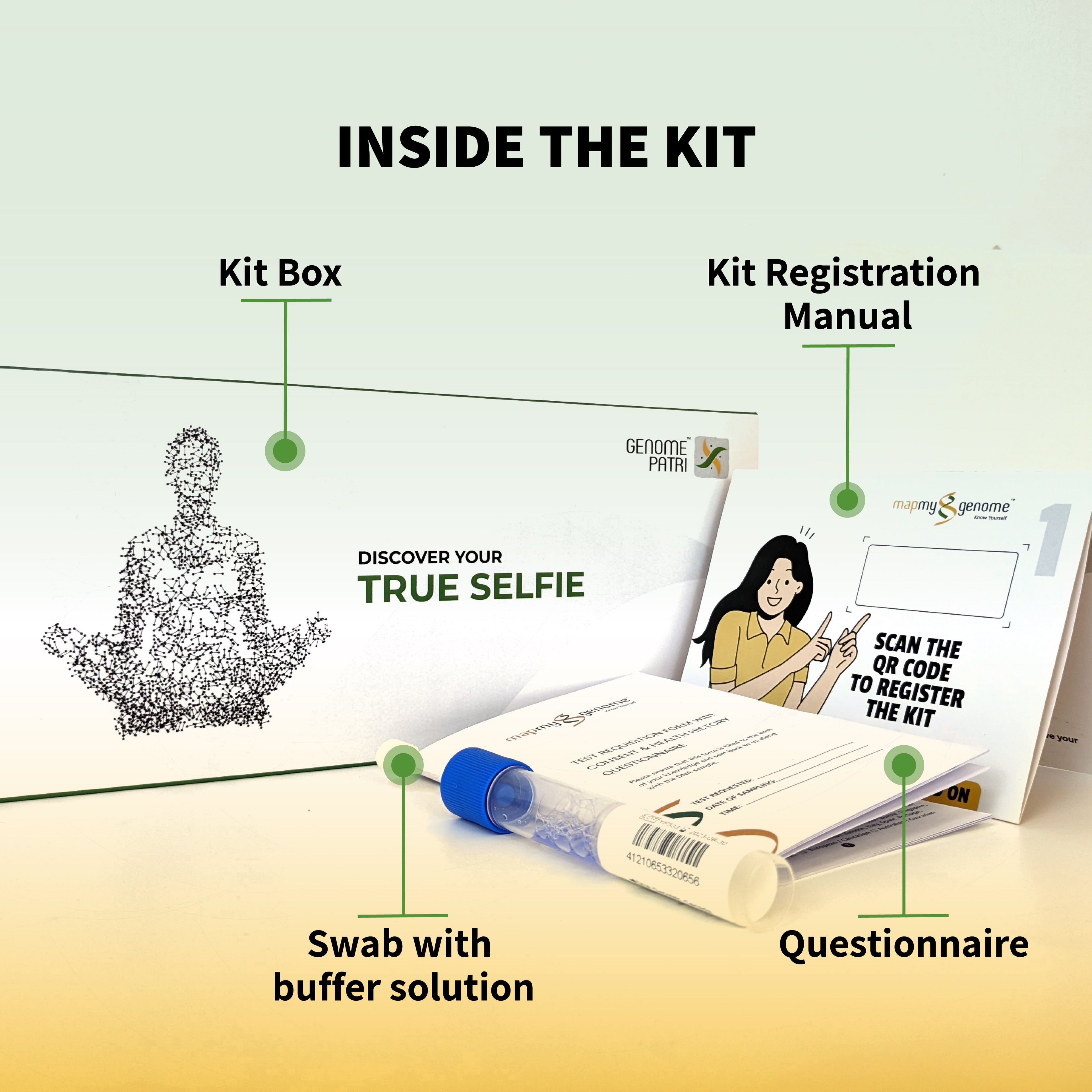
Genetic testing is revolutionizing healthcare, helping people uncover vital insights about their DNA. From predicting health risks to tracing ancestry, these tests unlock powerful knowledge about who we are and what the future may hold for our health. But what exactly is genetic testing, and how does it work? Let’s dive deep into the world of DNA testing and explore its many applications.
What is Genetic Testing?
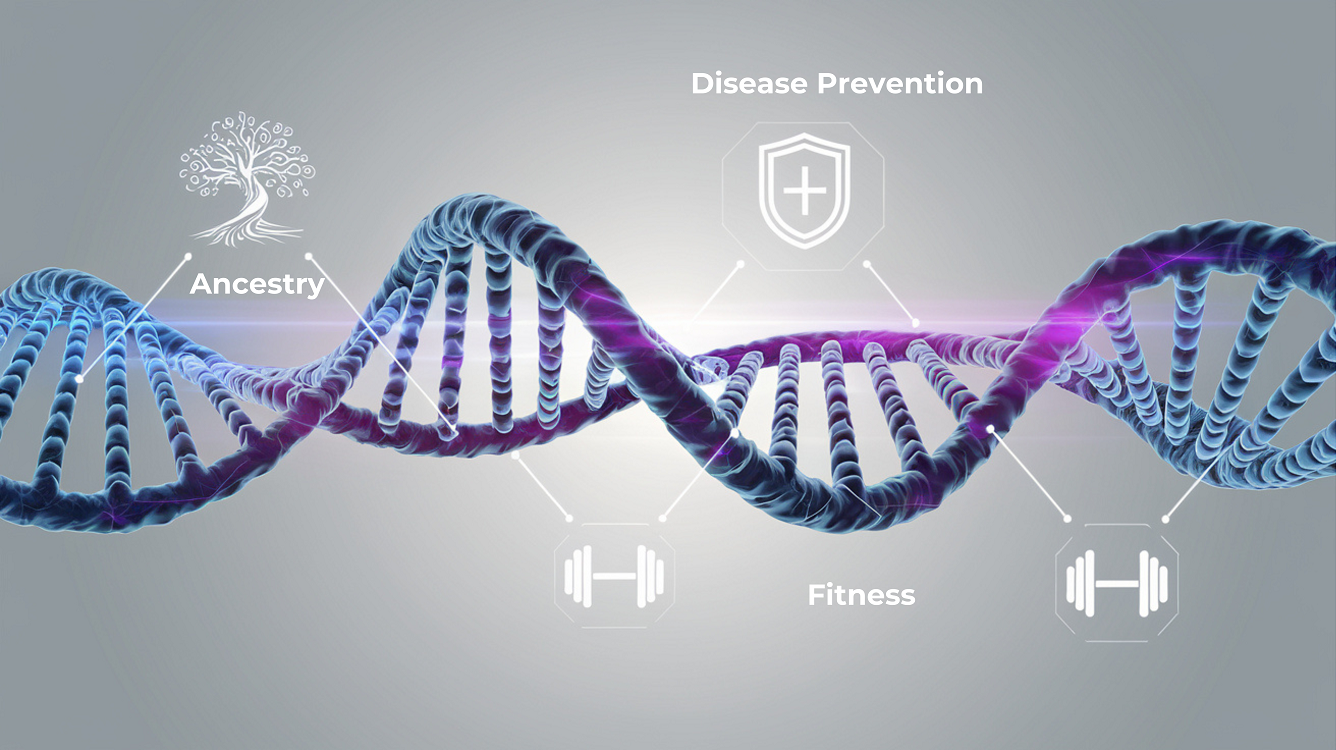
Genetic testing is a scientific process that analyzes your DNA, the blueprint of life, to identify variations in genes, chromosomes, or proteins. These variations can reveal valuable information about health conditions, inherited traits, and predispositions to diseases.
Key Focus Areas of Genetic Testing
-
Disease Risk Assessment: Predicts the likelihood of developing conditions like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
-
Carrier Screening: Helps determine if you carry genes for inherited diseases like cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia.
-
Ancestry Testing: Traces genetic lineage and ethnic background.
-
Pharmacogenomics: Determines how an individual responds to medications based on their genetic makeup.
-
Prenatal & Newborn Screening: Identifies potential genetic disorders in babies before or immediately after birth.
How Does Genetic Testing Work?
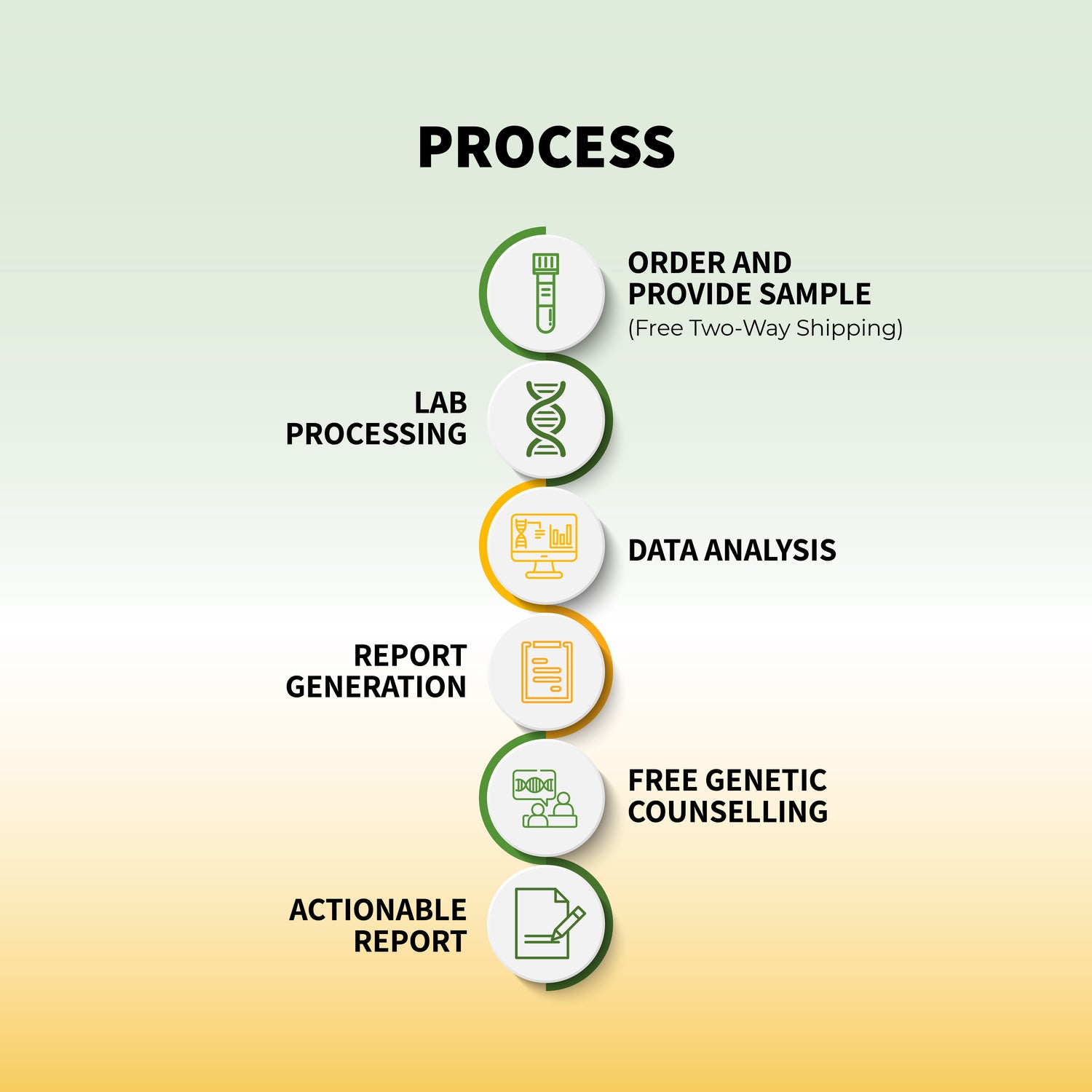
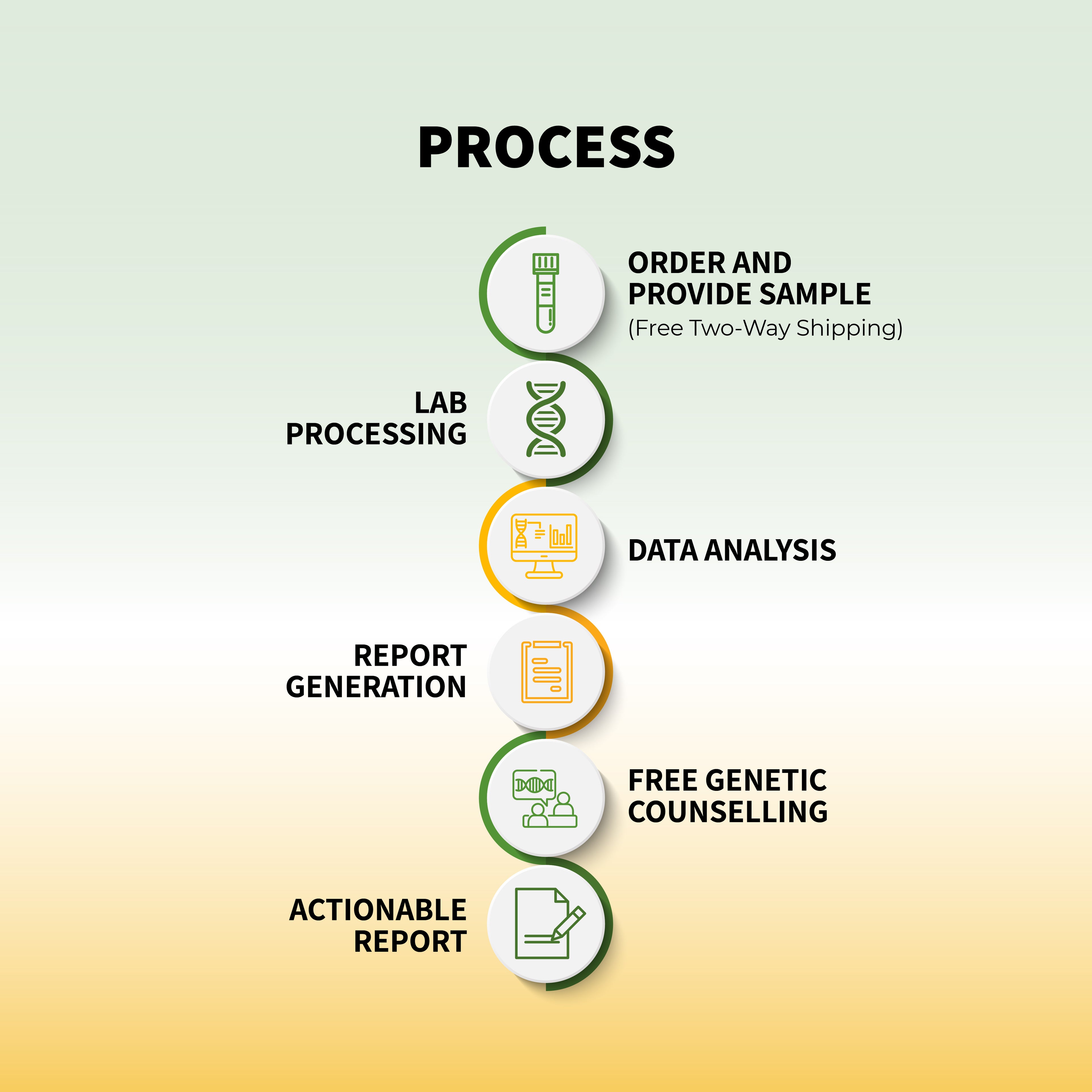
The process of genetic testing is simple and involves a few essential steps:
-
Sample Collection: A saliva, blood, or cheek swab sample is collected.
-
Laboratory Analysis: Scientists examine the DNA for genetic variations.
-
Results Interpretation: A genetic counselor or healthcare provider explains the findings.
-
Actionable Insights: Based on the results, individuals can take preventive or corrective health measures.
Types of Genetic Tests
1. Diagnostic Testing
Used to confirm or rule out a suspected genetic disorder. For example, genetic tests can diagnose Huntington’s disease or cystic fibrosis.
2. Predictive & Pre-Symptomatic Testing
Helps assess the risk of developing conditions like Alzheimer’s or certain cancers before symptoms appear.
3. Carrier Testing
Determines whether a person carries a gene for a genetic disorder that could be passed to their children.
4. Pharmacogenetic Testing
Analyzes how your body responds to medications, helping doctors prescribe the most effective treatments.
5. Ancestry & Ethnicity Testing
Uses DNA markers to trace lineage and heritage, connecting individuals to their ancestral roots.
6. Prenatal & Newborn Screening
Detects genetic abnormalities in unborn babies or newborns, ensuring early medical intervention if necessary.
Real-World Applications of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is not just for medical professionals—it’s changing lives worldwide. Here are some practical applications:
-
Preventive Healthcare: People can modify their lifestyle based on genetic predispositions to diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
-
Personalized Medicine: Doctors tailor treatments to a patient's unique genetic profile.
-
Family Planning: Couples can assess risks of passing on genetic disorders to their children.
-
Fitness & Nutrition: DNA-based diet and fitness plans optimize health and performance.
-
Forensic Science: Helps in solving crimes by identifying genetic evidence.
Pros of Genetic Testing
-
Early disease detection and prevention
-
Personalized treatment plans
-
Ancestry insights and family connections
-
Helps in medication effectiveness
Future of Genetic Testing
With rapid advancements in technology, genetic testing is becoming more affordable and accessible. AI-driven genome analysis, at-home DNA test kits, and precision medicine are shaping the future of healthcare.
FAQs About Genetic Testing
1. Is genetic testing safe?
Yes, genetic testing is a non-invasive and safe process using saliva, blood, or cheek swabs.
2. How accurate are DNA tests?
Most genetic tests are highly accurate, but interpretations should be done by professionals.
3. Can genetic testing predict all diseases?
Not all diseases are purely genetic; lifestyle and environment also play a role.
4. Do I need a doctor’s approval for a genetic test?
Some tests require medical supervision, while others can be done via direct-to-consumer kits.
5. How much does genetic testing cost?
Costs vary, ranging from $100 for basic ancestry tests to over $1,000 for comprehensive health screenings.
Conclusion
Genetic testing opens the door to personalized health and wellness, allowing individuals to take control of their future. Whether for ancestry exploration, disease prevention, or medication effectiveness, understanding your DNA is a powerful step toward better health and longevity.
Curious about your genetic makeup? Explore genetic testing today and take charge of your well-being!